Architecture
Ugly Belgian Houses
A chap named Hannes Coudenys has made his hobby of photographing deplorable architecture in his native Belgium into two books.
Click on the book names below to find them at Amazon.
You can read an explanatory essay by him here.
This is his Tumblr page.
His Instagram page.
Ugly Belgian Houses Book One

Ugly Belgian Houses Book Two

Posted By: Paul - Fri Mar 25, 2022 -
Comments (2)
Category: Architecture, Beauty, Ugliness and Other Aesthetic Issues, Books, Europe
Dr. Seuss House, Alaska
Video should start at the proper segment. Otherwise, minute 41.
Posted By: Paul - Sun Mar 20, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Architecture, Eccentrics
Frances Gabe’s Self-Cleaning House
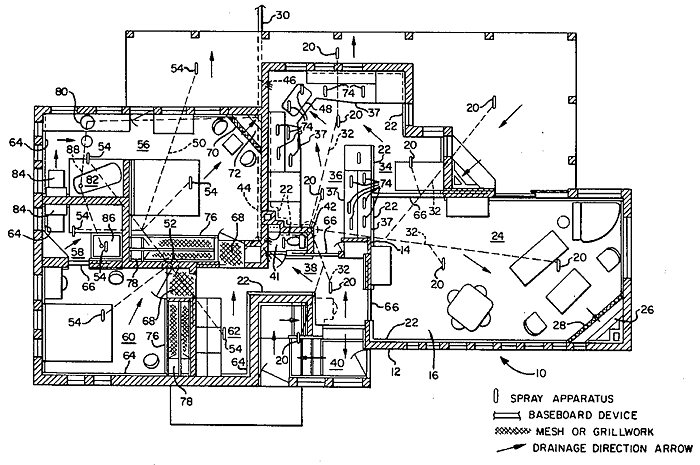
Frances Gabe had a vision of putting an end to housework. No more dusting or vacuuming. All a homeowner would have to do would be to push a button and the house would clean itself, as if the entire structure was a giant dishwasher.Of course, this meant that everything in the house had to be waterproofed. But it also meant that the actual dishwasher and clothes washer became redundant. Just hang dirty clothes in the closet and stack dishes in a cabinet — they'd get washed along with the rest of the house.
Gabe offered two stories for how she came up with the concept of the self-cleaning house. The first was that, as a newly married young woman, she once noticed a jam stain on the wall. Instead of scrubbing it off she decided to get a hose and sprayed it off.
The second story involved divine inspiration. After divorcing her husband she said that she was sitting, feeling despondent, and praying to God to provide her with some purpose to keep her going. Suddenly two angels appeared on her shoulders. And then, she said, "I picked up a pencil and began scribbling. I thought I was just doodling. Then I stopped and looked, and there was the self-cleaning house."
She received a patent (No. 4,428,085) for the self-cleaning house in 1984. She also transformed her own house in Newberg, Oregon into a prototype. From what I can gather, she never managed to make the entire house self-cleaning, but the kitchen could clean itself.
When she was alive she would offer tours of the house, but she died in 2016, and the new owners of the house haven't maintained its self-cleaning features.
Incidentally, Gabe was an invented name, so it's not what appears on her patent. Her full name, when married, was Frances Grace Arnholtz Bateson. She constructed 'Gabe' out of her initials.
More info: mit.edu, wikipedia
Posted By: Alex - Wed Feb 09, 2022 -
Comments (6)
Category: Architecture, Inventions, Patents, Baths, Showers and Other Cleansing Methods
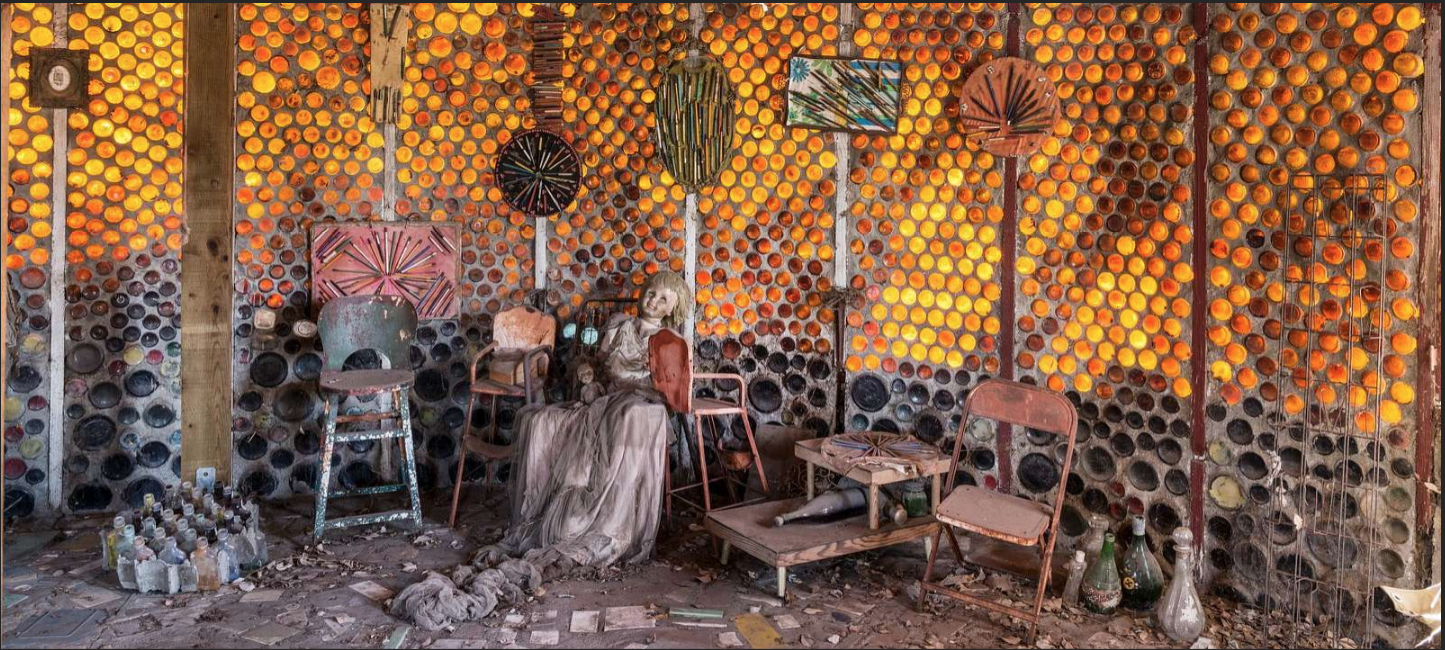
Grandma Prisbey’s Bottle Village
The official website.Many more pics here.


Posted By: Paul - Sun Jan 23, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Architecture, Eccentrics, Regionalism, Twentieth Century
Earth’s Black Box
On an empty plain in Tasmania there now sits a metallic structure filled with storage drives that is recording "every step we take" toward climate-change catastrophe. Its creators — marketing communications company Clemenger BBDO in collaboration with University of Tasmania researchers — describe it as "Earth's Black Box".Perhaps I'm too cynical, but I predict that the project is abandoned within 20 years and this turns into an architectural curiosity sitting in the middle of nowhere. I was going to say 10 years, but I'll be charitable.
More info: cnet.com, EarthsBlackBox.com

Posted By: Alex - Tue Jan 04, 2022 -
Comments (3)
Category: Architecture, Armageddon and Apocalypses, Technology
Colleen Moore’s Fairy Castle
Still on display at the Chicago Museum of Science & Industry. Lots of great pix at this link.
Source of article below.
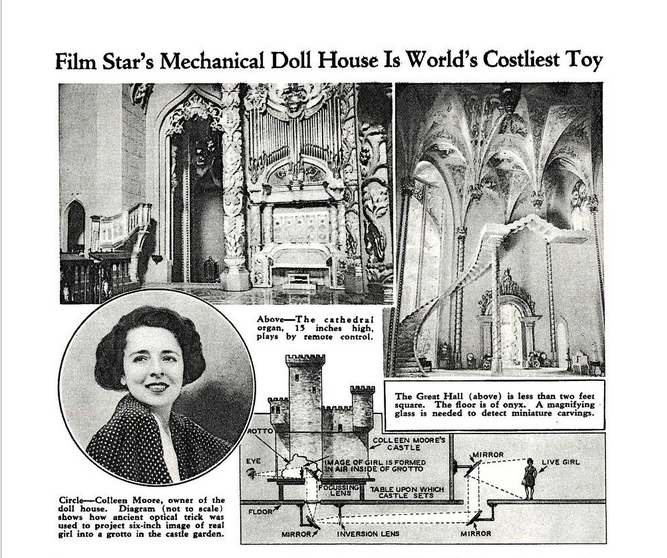

Posted By: Paul - Tue Nov 23, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Architecture, Charities and Philanthropy, Enlargements, Miniatures, and Other Matters of Scale, Hollywood, Museums, 1930s
Martian Blood Concrete
Researchers at the University of Manchester have proposed that future settlers on Mars can create concrete by mixing Martian dust with their own blood and urine. Details from globalnews.ca:The blood-and-dust mixture alone is equivalent to concrete, but researchers say it becomes even stronger when human urea is added to the mix...
Roberts and his team say that animal blood could eventually replace human blood in Martian construction projects, but that would only happen after we send cows to Mars.

Experimental 'astrocrete' made from blood and dust
We've posted before about the use of blood to make concrete. Charles Laleman was granted a patent for this in 1980, but the practice goes all the way back to Roman times.
Posted By: Alex - Sat Oct 02, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Architecture, Patents, Space Travel, Blood
The Highest Streakers
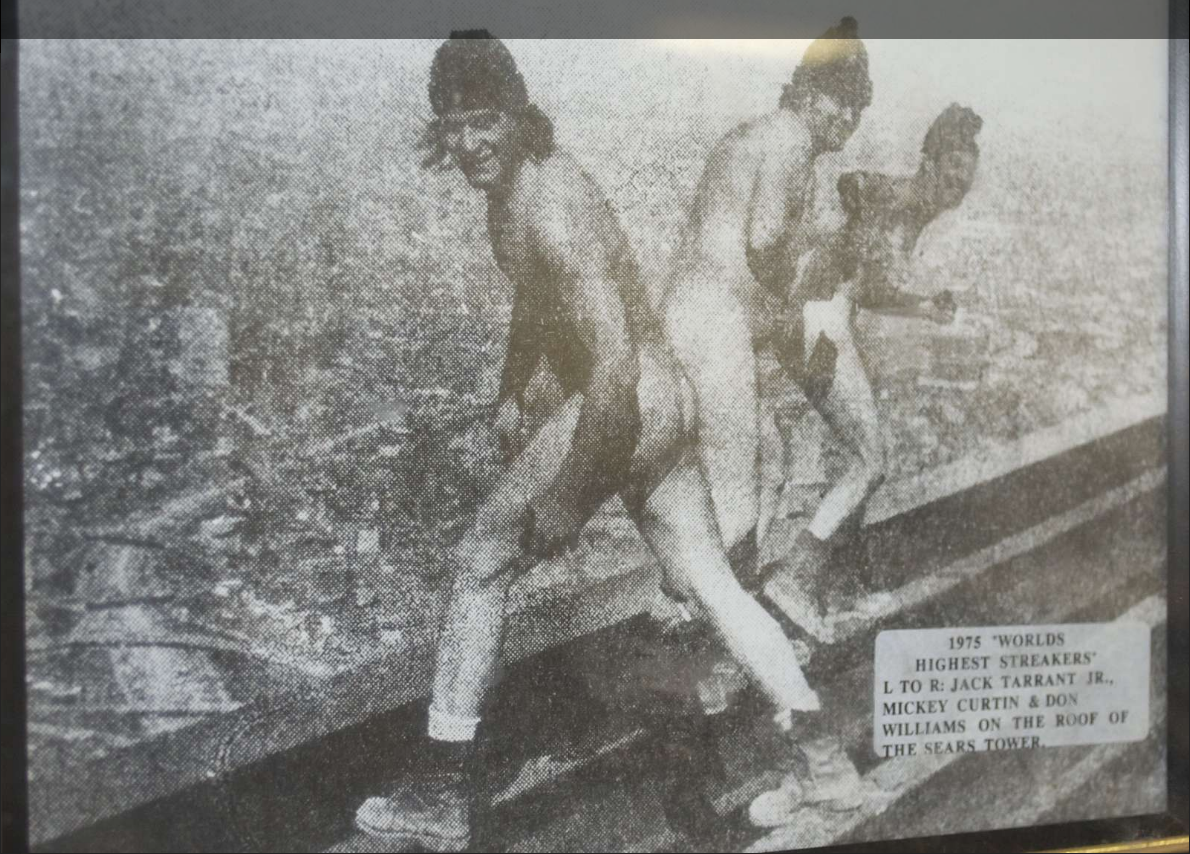

I can find absolutely no supporting documentation of this event, but the photo comes from the Library of Congress, so it must be true!
Posted By: Paul - Sat Jul 24, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Architecture, Fads, Public Indecency, 1970s
The Winooski Dome
In 1979, officials in Winooski, Vermont applied for a $55,000 federal grant to study the possibility of building a dome over the entire city. They explained that a dome might slash the cost of heating Winooski's buildings by up to 90 percent.They didn't actually have a plan for how the dome would be built, but they eventually enlisted the help of architect John Anderson who came up some ideas. Details from UnofficialNetworks.com:
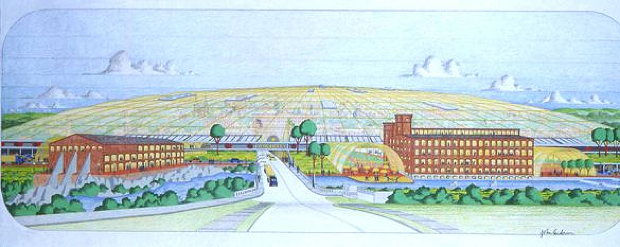

Posted By: Alex - Fri Jul 23, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Architecture, 1970s
Dirty Toilets Prompt Relocation
This is like the old joke about selling your car when the ashtrays get full.

Posted By: Paul - Sun Jun 27, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Architecture, Business, Advertising, Hygiene, Twentieth Century

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




