Death
Robin orders sparrow to be shot
Aug 1979: Frustrated by a sparrow that was chirping in his church when a guitar recital was going to be recorded, Rev. Robin Clark ordered the bird to be shot.I'm sure that, after that, no one made a sound during the recital.

The Vancouver Columbian - Aug 8, 1979
I couldn't find a recording of the sparrow-death recital, but here's some music by Konrad Ragossnig.
Posted By: Alex - Fri Mar 31, 2023 -
Comments (3)
Category: Animals, Death, Music
Unlikely Reasons for Murder No. 13

Source: The News and Observer (Raleigh, North Carolina)03 Apr 1912
Posted By: Paul - Thu Mar 23, 2023 -
Comments (3)
Category: Death, Money, Teenagers, 1910s
The Hurricane Party of 1969
Based on the press coverage from 1969, it sounds like the couples who remained in the path of Hurricane Camille to have a "hurricane party" certainly deserved to become Darwin Award winners (bestowed on them in 2000 by Wendy Northcutt in her Darwin Awards book)."The last time I went up to try to get them out, the water was just over the sea wall. They were having a good time and they wouldn't leave. That's the last anybody saw of them," he said.

Orlando Evening Star - Aug 19, 1969
But digging deeper into the story, thirty years after the hurricane people began challenging the tale of a "hurricane party." According to the debunkers, there was no party, and the people who stayed had been told by the apartment manager that the building could withstand a hurricane because it was a designated Civil Defense shelter.
One apartment resident who survived the hurricane continued to insist that the people on the third floor had been having a party. But this woman also claimed insanity as the reason she killed her 11th husband. So not the most credible witness.
More info: Hurricane Camille party in 1969: Fact or fiction? -- Hurricane Party

image source: Acts of God: the Old farmer's almanac unpredictable guide to weather and natural disasters
Posted By: Alex - Tue Mar 21, 2023 -
Comments (6)
Category: Death, Dinners, Banquets, Parties, Tributes, Roasts and Other Celebrations, 1960s, Weather
Running Bear
The singer's Wikipedia page.
Posted By: Paul - Sat Mar 18, 2023 -
Comments (8)
Category: Death, Music, 1960s, Native Americans
No seatbelt
1987: While making a safety film about the benefits of wearing a seatbelt, Anthony Galati lost control of his car and crashed, dying of his injuries. He wasn't wearing a seatbelt.More info: AP News

click to enlarge

Bowling Green Sentinel Tribune - May 18, 1987
Posted By: Alex - Fri Mar 17, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Accidents, Death, 1980s, Cars
Thirty Years Among the Dead
The Wikipedia page for Wickland, where we learn:Wickland turned away from conventional medical psychology and toward the belief that psychiatric illnesses were the result of influence by spirits of the dead. Wickland came to believe that a large number of his patients had become possessed by what he called "obsessing spirits", and that low-voltage electric shocks could dislodge them, while his wife Anna acted as a medium to guide them to "progress in the spirit world". Spiritualists considered him an authority on "destructive spirits" and he wrote a book in 1924, Thirty Years Among the Dead, detailing his experiences as a psychical researcher.[3]
Wickland was convinced that he was in contact with a group of spirits known as the "Mercy Band" who would remove the possessors, and help them in the spirit world. Psychologist Robert A. Baker listed Wickland and Arthur Guirdham as early psychiatrists who preferred to "ignore the science and embrace the supernatural".[4]
Read his book at the Internet Archive.


Posted By: Paul - Mon Mar 13, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Death, Supernatural, Occult, Paranormal, Books, 1920s
The Foreshadowed Death of Gloria Dickson
In 1943, actress Gloria Dickson had a sizable part in THE CRIME DOCTOR'S STRANGEST CASE.The scene to focus on starts below at 44:23. Gloria is married to a man who's very careless with matches, even starting fires in bed. She remarks that she's been "almost cremated."
Two years later, Dickson would die in a domestic fire in her bedroom, apparently started by a stray match.
Newspaper clip source: Fort Worth Star-Telegram (Fort Worth, Texas) 11 Apr 1945, Wed Page 3

Posted By: Paul - Thu Feb 16, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Death, Domestic, Fate, Predetermination and Inevitability, Hollywood, Predictions, 1940s
Crestone End-of-Life Project
The only place in the United States where it's legal to have an open-air cremation is the town of Crestone, Colorado. And specifically at the "outdoor human cremation facility" maintained by the Crestone End-of-Life Project.However, if you're not from there, they won't cremate you. As explained by US Funerals Online:

Posted By: Alex - Fri Jan 13, 2023 -
Comments (1)
Category: Death
Follies of the Madmen #552
Please note the last cartoon in this ad (magnified below). Man attempts to kill mother-in-law by darkening the stairwell. Everything A-OK!Source.


Posted By: Paul - Mon Jan 09, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Death, Domestic, Technology, Advertising, 1950s
The Anomaly That Wouldn’t Go Away
In medical literature, the "anomaly that wouldn't go away" refers to a finding published in 1978 by a group of Welsh doctors (Cochrane, St Leger, and Moore). They had set out to examine the relationship between health services and mortality in the major developed countries, but in doing so they came across a correlation that surprised them — the more doctors there were per capita, the higher was the rate of infant mortality.The correlation wasn't a weak one. In fact, for infant mortality it was the strongest correlation in their study. The number of doctors per capita seemed to have a stronger negative impact on infant mortality than did the level of cigarette or alcohol consumption in the population.
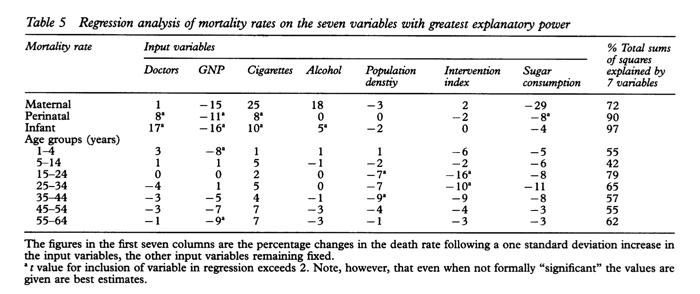
Obviously the researchers found the correlation unsettling since, ideally, more doctors should result in fewer, not more, infants dying.
So why would more doctors correlate with higher infant mortality? The three doctors did their best to figure this out:

As the above passage indicates, they didn't think it was plausible that doctors themselves were somehow responsible for the elevated infant mortality, but nor could they come up with a satisfactory explanation for the correlation. So they called it "the anomaly that wouldn't go away."
I'm not sure if the correlation still holds true. I believe it still did about twenty years ago. Unfortunately much of the relevant literature is locked behind paywalls.
Over the years there have been quite a few attempts to explain the anomaly. I've listed two below. Again, I'm not sure if one has been accepted as THE explanation. So the anomaly may still persist.
It occurred to us that some of the countries richly endowed with physicians may obtain their large supplies by having bigger medical schools, larger classes, and thus less individual instruction of the medical student. The consequence could be a poorer standard of medical practice, the influence of which would be evident in the mortality of the younger age groups where the outcome of disease is most susceptible to the physician's skill.
The explanation proposed here is that, as compared with other regions, the expectation of opportunities in the growing industrial cities initially attracts an over supply of doctors. Once in practice, doctors in new regions enjoy fewer economies of scale, which means that they are more numerous as compared with the mature regions. These same industrialising cities attract rural immigrants whose health habits and supports break down in the context of city life. Thus, the places with the most doctors also have the highest death rates, but the two variables are associated only by common location.
More info (pdf): Cochrane, Leger, & Moore, "Health service 'input' and mortality 'output' in developed countries."
Posted By: Alex - Fri Dec 23, 2022 -
Comments (9)
Category: Babies, Death, Medicine

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




