Health
Impact Therapy

Shamokin News Dispatch - Aug 31, 1968
LONDON (AP) — Dr. John Tracy says if you can't cure it any other way, hit it.
Tracy explained in today's issue of the Practitioner Medical Journal that he uses sandbags to bash his patients into shape. He calls it "impact therapy."
Tracy says that repeated blows with a 20-pound sandbag, carefully timed and judged, send pressure waves through joints that cure aches and pains.
Posted By: Alex - Wed Jun 13, 2018 -
Comments (5)
Category: Health, Medicine, 1960s
Brain fluid leak
In the news recently, Kendra Jackson who had long been suffering from chronic sneezing and a runny nose, was diagnosed as actually having a brain fluid leak — after doctors had been telling her for years that she just suffered from allergies. A surgical procedure managed to fix the problem.(more info: ketv.com)
Reminded me of the 1936 case of "sneeze girl" that I posted about 2 weeks ago. Perhaps Sneeze Girl was also suffering from some kind of brain fluid leak.
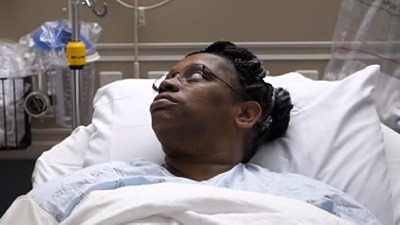
Kendra Jackson
Posted By: Alex - Thu May 31, 2018 -
Comments (0)
Category: Health
Sneeze Girl
From Time magazine, Dec 14, 1936:To see if allergy to some substance caused the sneezing, Washington doctors scratched her skin some 80 times, rubbed into the scratches hay pollen, flower pollen, pulverized cat fur, dog hair, house dust, food extracts, dozens of substances.
Skin tests failed to reveal any specific allergy. A Washington doctor cut out the adolescent's tonsils, with no effect on the sneezing. Other specialists could find nothing unusual in her lungs or nervous system.
Lay cures for sneezing which Mary Cleer was urged to try included wearing a "magnetic" letter pinned to her night dress, looking down the bridge of her nose at pieces of bright silk held close to the tip, clipping an electrified wire to her nose and toes, getting tattooed, taking snuff.
Last week when Mary Cleer went to Johns Hopkins Hospital, the great medical faculty there had never before treated or even seen a girl who sneezed so persistently. Johns Hopkins specialists began a new series of tests. A psychiatrist examined the girl and summoned her parents to analyze their mental and emotional makeups. Mary underwent fluoroscopy, blood testing, other examinations. A gynecologist also took her in charge, for the nasal and genital tissues are histologically related. The mucous membranes of the nose swell during sexual excitement. This well-known phenomenon gives rise to a theory that the noses of many little girls become sensitive as they turn into young womanhood, and that this makes such girls sniff, lisp or pamper their noses in an apparently affected manner, and that this overture to womanhood causes an occasional girl to sneeze uncontrollably. That, a gynecologist might guess, was the trouble with Mary Cleer, 13.
Apparently the sneezing eventually stopped of its own accord. No one ever figured out what the cause was.

Decatur Daily Review - Dec 3, 1936

(left) Alexandria Town Talk - Oct 27, 1936
(right) Daily Clintonian - Dec 8, 1936
Posted By: Alex - Thu May 17, 2018 -
Comments (1)
Category: Health, Medicine, 1930s
Cho-Cho the Health Clown
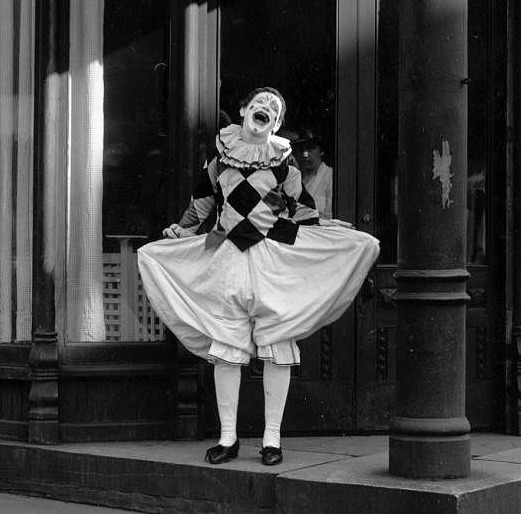

Cho-Cho was a "health clown" who toured the USA during the 1920s, visiting classrooms, and trying to encourage kids to eat more vegetables, take baths, and brush their teeth. In a way, he was like the opposite of Ronald McDonald (Ronald being a clown who encourages children to eat junk food).
CHO stood for "Child Health Organization," which was the group that dreamed him up and sent him out. Some more info from the book Children’s Health Issues in Historical Perspective:
All three travelled to elementary and secondary schools, as well as exhibitions, fairs, and "any place where children were gathered together. A less traditional figure was CHO's pseudo-professor Happy (played by Clifford Goldsmith), who entertained child and adult audiences with snappy health maxims.
Happy, the Health Fairy, and the cartoonist worked well within the boundaries of CHO's program, but when the clown who played Cho-Cho began to regard himself "as a real authority on diet, hygiene, and even the morals of childhood," and deviated from his "carefully learned lines," the organization had to find a new Cho-Cho.


Popular Science Monthly - Feb 1920
Posted By: Alex - Thu Mar 22, 2018 -
Comments (2)
Category: Clowns, Health, 1920s
Anti-Puberty Pill
In 1969, British health officer Dr. J.V. Walker proposed the development of a pill "to give young people to delay the onset of sexual maturity until they leave college and could earn their own living." Walker felt certain "it should not be difficult to develop a hormone preparation for the job."Such a pill would certainly change the college experience for most people.

Akron Beacon Journal - June 1, 1969
A bit of research revealed that this J.V. Walker was Joseph V. Walker, health officer of Darlington. I couldn't find a fuller description of his anti-puberty pill, but I did come across a letter he sent to the Health Education Journal (March 1, 1970) in which he worried that young women would develop into "promiscuous addicts" if they didn't preserve their virginity until marriage. I suppose his pill would help with that goal as well.

Posted By: Alex - Tue Mar 13, 2018 -
Comments (10)
Category: Health, 1960s, Universities, Colleges, Private Schools and Academia
Washroom Infection
In the early 20th century, it was widely believed that dirty bathrooms were a primary cause of the spread of disease, particularly sexual disease. One result of this belief, apparently, was the adoption of U-shaped toilet seats in public bathrooms, since it was thought that these were more hygienic.Read more about this at The Weeklings.

Posted By: Alex - Fri Feb 02, 2018 -
Comments (7)
Category: Health, Disease, Hygiene, Advertising, 1930s
LadyCare Menopause Magnets
The manufacturers of LadyCare Magnets claim that women can ease the symptoms of menopause by magnetizing their underwear.I guess it can't hurt, but might look a bit odd if random metallic objects (forks, paperclips, etc.) are attracted to your crotch.
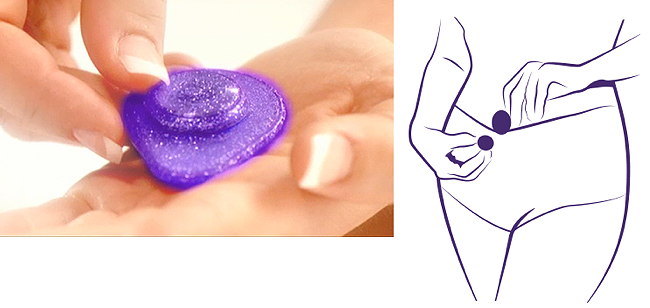
Posted By: Alex - Tue Jan 02, 2018 -
Comments (4)
Category: Health, Underwear
Showgirls With Hiccups
Posted By: Paul - Tue Sep 12, 2017 -
Comments (4)
Category: Health, 1960s, Screams, Grunts and Other Exclamations
Toilet Tissue Illness
In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Scott Tissues ran an advertising campaign that sought to convince the American public that there was such a thing as 'Toilet Tissue Illness,' and that it was one of the great public health crises of the time. Toilet Tissue Illness was caused by using cheap toilet paper. It could lead to serious complications, possibly requiring rectal surgery to fix. So the ads suggested.The most notorious ad in the campaign was the 'black glove' ad below.

Here's some background info about the Scott Tissue campaign from Richard Smyth's Bum Fodder: An Absorbing History of Toilet Paper:
And a few of the other ads featured in the campaign:


Posted By: Alex - Thu Jul 20, 2017 -
Comments (4)
Category: Health, Advertising, 1920s, 1930s
Caffeinism
March 1985: Sgt. Joseph Mitlof of the NYPD realized that the 30 cups of coffee a day he was drinking might have been contributing to his anxiety problems. In fact, he was suffering from "caffeinism."
Tallahassee Democrat - Mar 20, 1985
I had never heard of such a thing as "caffeinism," but it turns out the term is over 100 years old. A 1979 article in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis offered the following definition:

Burlington Daily Times - Mar 5, 1968
I only drink one cup of coffee a day, first thing in the morning. I think I'm good.
Posted By: Alex - Mon Jun 19, 2017 -
Comments (3)
Category: Drugs, Health

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




