Inventions
Horizontal Theater
Back in 1945, Thomas Curtis Gray of Washington, DC was granted a patent for a theater in which the patrons would view the movie while lying-down. To facilitate this, the movie was projected onto a screen anchored to the ceiling.Gray argued that his horizontal theater had several advantages over a traditional theater. First, it would be more comfortable to watch a movie while reclining. Second, a patron's view would never be obstructed by someone in front of them. And finally, the screen could be located at a closer-to-equal distance from all viewers.
I've never heard of a horizontal theater being built. But arguably his patent foreshadowed the rise of the modern-day luxury cinemas where you can relax in seats that recline almost all the way back.

Posted By: Alex - Sun Aug 09, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: Architecture, Inventions, Patents, Movies, 1940s
Mother Heart
Japan's "crazy inventor" Hiroshi Majima invented this odd device:The tot apparently feels secure and reassured, stops yelling and drifts off to sleep without another whimper.
Bed-wetting is also greatly reduced, inventor Majima finds.
"Mother Heart" now sells abroad, not just on Japan's domestic market alone. Ready-made markets, Majima says, have been found in the Mediterranean countries, like France, Italy, and Spain, where mothers are especially close to their infants, and vice versa.


Allentown Morning Call - Sep 16, 1965
We previously featured another one of Majima's strange inventions on WU: the Cat Mew Machine.
Posted By: Alex - Wed Jul 29, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: Babies, Inventions, 1960s
Corn Vest
Rick Atkinson, Jr. of Canton, Georgia recently received a patent for a vest designed to hold "bulk product," such as corn. The corn goes in pockets at the top of the vest, and can then be dispensed from pockets at the bottom.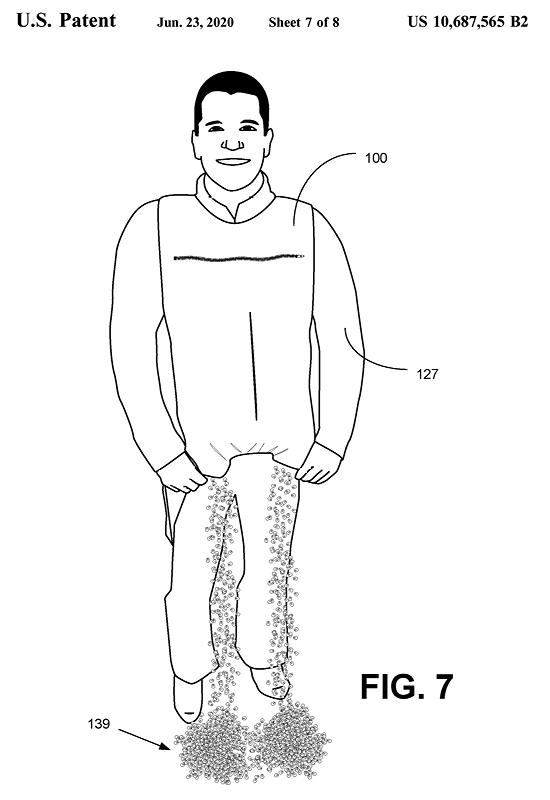
Atkinson explains that he designed the vest for hunters who "may carry corn, soybeans, grains, and/or other bulk products to attract deer, hogs, turkey, bear, and/or other wild game." Instead of carrying large bags of corn around, they can simply wear the corn and dispense it as they walk around.
I imagine this could also be useful for feeding pigeons in the park.
Posted By: Alex - Thu Jul 23, 2020 -
Comments (5)
Category: Fashion, Food, Inventions, Patents
Mark Korven and His Apprehension Engine
Full story here.
Posted By: Paul - Wed Jul 01, 2020 -
Comments (3)
Category: Horror, Inventions, Movies, Special Effects, Technology
Apparatus for temporarily immobilizing earthworms
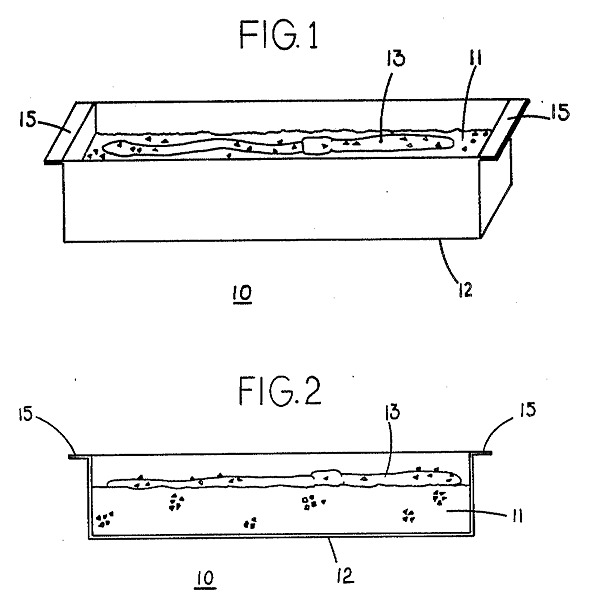
Worms wiggle. This can make it hard for fishermen to impale them on a hook. But in 1989, Loren Lukehart of Boise, Idaho offered a solution. He received a patent (No. 4,800,666) for a method of "dewiggling" earthworms.His invention was essentially a rectangular box full of sand. From his patent:
Once the sand coated earthworm is immersed in water, the sand rinses free and the earthworm resume its normal wiggly character.
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jun 28, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: Inventions, Patents, Sports, 1980s
Animal Trap
Jason Alexander Williams didn't mess around when it came to killing rodents. His 'animal trap' (patented in 1882) shot them dead:The object of my invention is to provide a means by which animals which burrow in the ground can be destroyed, and which trap will give an alarm each time that it goes off, so that it can be reset.
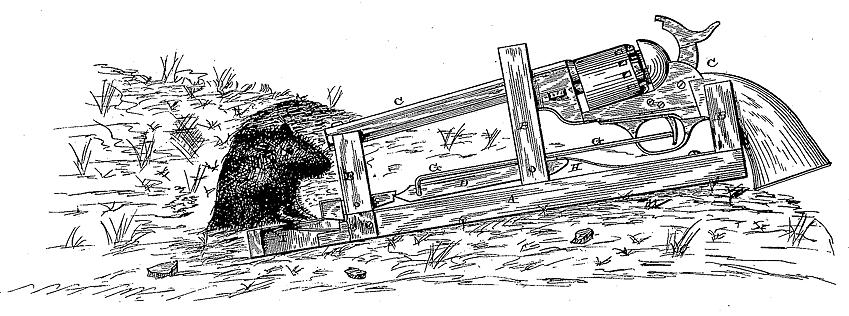
And his invention didn't just kill rodents. Williams noted:
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jun 21, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Animals, Inventions, Patents, Nineteenth Century
Man-Catching Tank
Stanley Valinski's "man-catching tank," for which he received a patent in 1921 (#1,392,095), looked a bit like a dalek prototype.He imagined it would be used in banks for catching and holding burglars. It consisted of an armored watchbox concealing an armed watchman who could peer out through peep holes. The entire device moved on electric-driven wheels, which the watchman could steer. Upon spotting a burglar, he would maneuver the tank into position and then grasp the criminal with six enormous steel claws attached to the side of the machine.
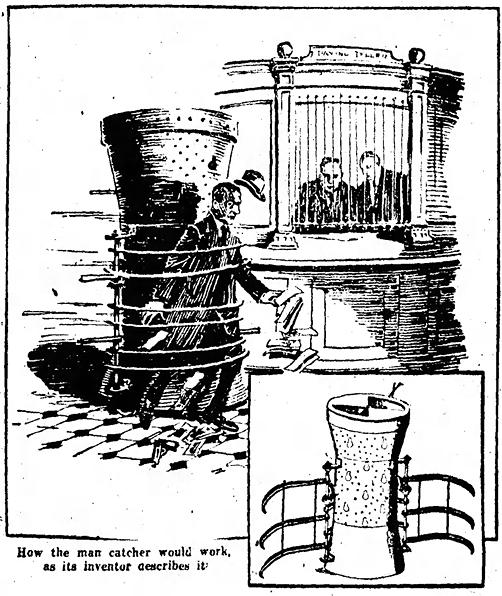
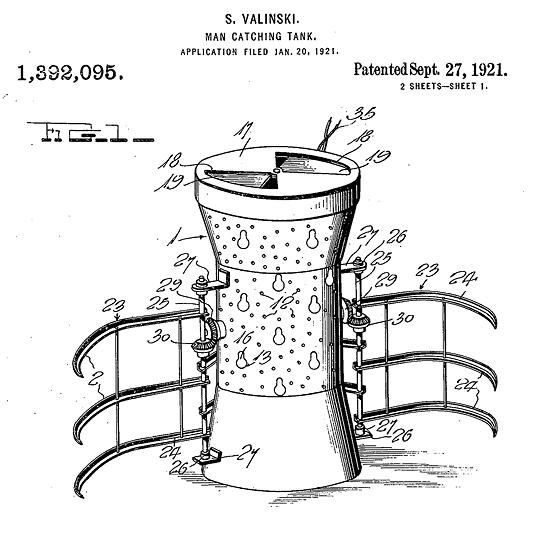

Wichita Daily Times - Dec 18, 1921
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jun 14, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: Crime, Inventions, Patents, 1920s
The Animan
It's now 2020. Where are our bipedal TVs?

Source: Popular Science - June 1988
Posted By: Alex - Mon Jun 08, 2020 -
Comments (7)
Category: Inventions, Television, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, 1980s
Hand Sanitizer Holster
Paula Russo was recently granted patent #10653232 for a "hand sanitizer holster," which seems like a timely invention for the age of covid, although she must have begun the patent process long before covid-19 was known.
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jun 07, 2020 -
Comments (6)
Category: Hygiene, Baths, Showers and Other Cleansing Methods, Inventions, Patents
Freeze-Dried Human Bodies
Philip Backman's 1978 patent describes a process for freeze-drying human bodies.The problem with freeze-drying any large animal is that there's not enough surface area to allow for rapid freeze-drying. So, to increase the surface area, Backman explained that it would first be necessary to freeze the body and then smash it into small pieces in a hammer mill. Once the body had undergone this "surface enhancement," it could be rapidly freeze-dried, which would remove the water in the body, reducing its weight by 95%. The resulting remains could be kept in an urn, just like cremated remains.
Backman argued that his freeze-drying process had all the advantages of cremation (in terms of reducing the body to a compact size), but cost less. However, the funeral industry apparently didn't like the idea of running bodies through a hammer mill.


Posted By: Alex - Sun May 31, 2020 -
Comments (6)
Category: Death, Inventions, Patents, 1970s

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




