Patents
Ads between telephone rings
I can only imagine how annoying it would be to have to listen to advertisements between rings whenever you phoned someone. And unfortunately the technology to do this has been developed. Neil Sleevi was granted a patent for it in 1989 (Patent No. 4,811,382), and Bell Atlantic promptly bought the rights to it.
Faced with public outcry, Bell Atlantic subsequently claimed that, even though they did buy the rights to the patent, they never had any intention of inserting ads between telephone rings, dismissing the entire notion as a silly rumor. But I'm pretty sure they would have done it if they had thought they could get away with it.
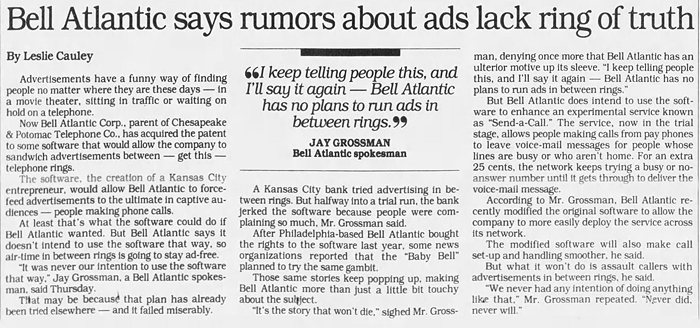
Baltimore Sun - Dec 14, 1991
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jan 02, 2022 -
Comments (5)
Category: Technology, Telephones, Advertising, Patents, 1990s
Method of executing a tennis stroke
In 1999, Kevin and George Repper were granted a patent (No. 5,993,336) for a "method of executing a tennis stroke". The method consisted of hitting a tennis ball while kneeling on the right knee — that knee being protected by a kneepad.This raises two questions. First, how did they possibly obtain a patent for this? And second, why did they bother getting a patent for this? Did they seriously expect other tennis players to license this method from them?
I don't know the answer to the first question, but I have a hypothesis about the second. Some googling reveals that George Repper was a patent attorney while his son, Kevin, was on a high-school tennis team. So my guess is that the patent was some kind of father-son bonding experience, with the father showing his son how to obtain a patent. And it seems like the son is also now a patent attorney.

Posted By: Alex - Sun Dec 19, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Inventions, Patents, Sports, 1990s
The Beachette
Esther Brown was granted a patent (No. 2,266,684) in 1938 for the "beachette," which was a wearable beach umbrella. A beachgoer could wear the fabric of the umbrella as a skirt/cape/hat combo. The pole doubled as a cane. When they got to the beach it could all be assembled into an umbrella.The problems I see: a) you've still got to carry the pole; and b) I bet assembling/disassembling the thing was a nuisance.
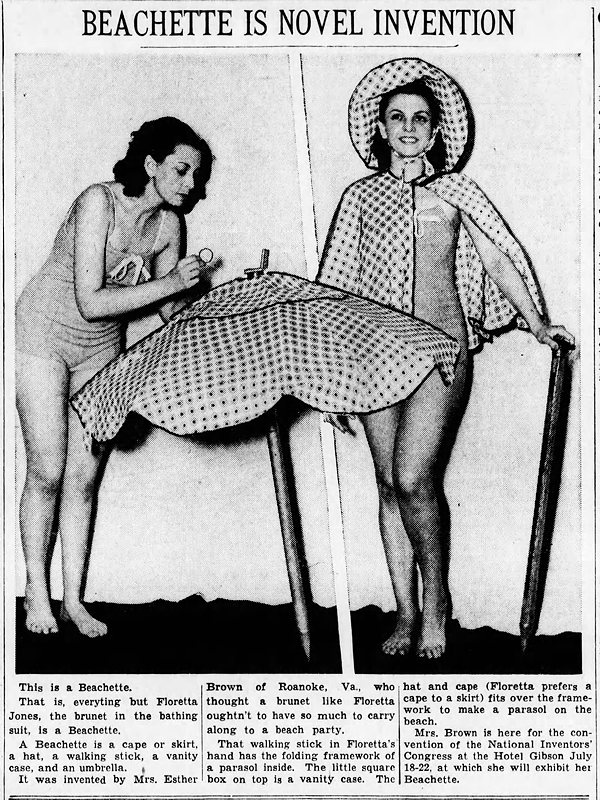

Cincinnati Enquirer - Jul 8, 1938
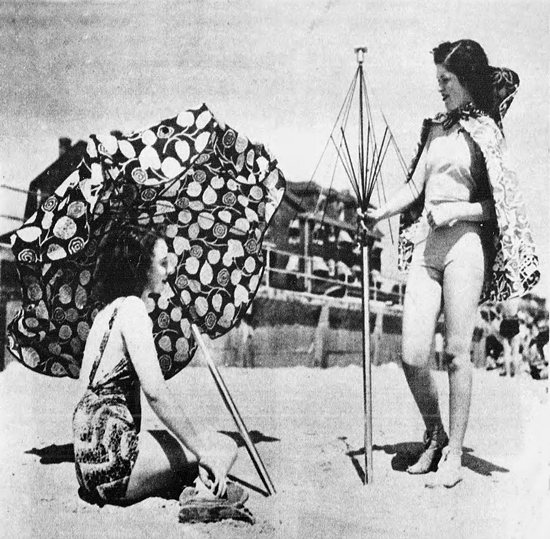

Pittsburgh Press - Sep 25, 1938
Posted By: Alex - Mon Dec 13, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Fashion, Inventions, Patents, 1930s
The Patented Carrot Rectal Dilator
In 1927, the Canadian patent office granted an unusual patent (CA 259317) to George L. Kavanagh. It was unusual because, while most patents describe some new type of gadget or gizmo, Kavanagh's invention simply consisted of a method of using a carrot.The problem Kavanagh had set out to solve was that of constipation in the elderly. The way he saw it, our rectums tend to grow more inelastic and shrunken as we age, and this leads to constipation. The solution, he concluded, was "gently dilating the anus and rectum until the organs are restored to their youthful size."
But what could be used as a dilator? Preferably something inexpensive and readily obtainable. That made him think of carrots.
A summary from his patent:

An added benefit of carrots, he noted, was that they come in a variety of different sizes. This would allow one to start with small carrots and work up to larger ones "until the desired result is obtained."
Unfortunately, Kavanagh submitted no drawings with his patent. But I did find a chart that provides a size comparison of different types of carrots, which could be potentially useful for anyone who wants to try out Kavanagh's method at home on an elderly relative.
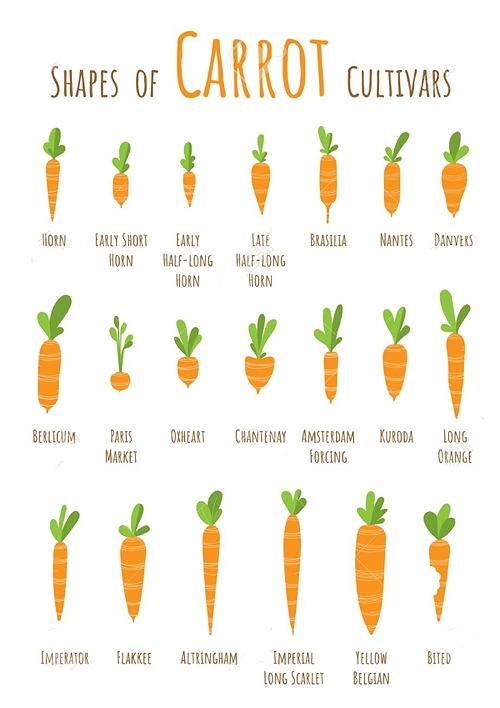
image source: 123rf.com
Update: Kavanagh also got a US Patent (No. 1,525,505) for his invention.
Posted By: Alex - Wed Nov 24, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Health, Inventions, Patents, Vegetables, 1920s
Double-Heeled Shoe
Patent No. 7,574,819, granted to Jin Rie of Los Angeles:
But why stop at two heels when you could have seven?

'Cleat Heels' from Jean Paul Gaultier's Spring 1993 collection
Posted By: Alex - Tue Nov 16, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Patents, Shoes
The Gramocar or Record Runner
The Gramocar has gone under a variety of different names: Chorocco, Record Runner, Soundwagon, and Vinyl Killer. But I like Gramocar the best.It was invented in the 1970s by a team at Sony who had the idea that instead of playing a vinyl record by spinning the disc and keeping the needle stationary, it would be possible to keep the disc stationary and move the needle. They designed the moving needle as a miniature VW van, with built-in speakers, that drove in circles around the surface of a record.
Sony got a patent on the invention (US4232202) but was initially reluctant to manufacture it, saying, "We are a hi-fi company, not a toy company." But they changed their mind, and some were sold in Japan. In that way, the Gramocar gained enough of a following that other manufacturers eventually began making them. And you can still buy one today at RecordRunner.jp.
More info: New Scientist - Feb 5, 1981

Posted By: Alex - Mon Nov 08, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Music, Technology, Patents, 1970s, Cars
William Redgrave’s Safety Travelling Cap
The British patent office granted William Redgrave two patents. The first (No. 2888 - 1853) was for a "safety travelling cap". The second (No. 762 - 1859) was for a "pillow travelling cap". However, the two patents seem to describe the same invention. They just emphasize different uses for it.Redgrave's patented cap consisted of three air-tight, circular tubes that would wrap around a wearer's head. His idea was that this would provide a measure of safety for travelers, because if the traveler fell the inflated tubes would cushion his head:
The cap could also serve as a pillow (thus, the second patent):
Finally, Redgrave noted that the cap was "an excellent invention for lunatics." Presumably because lunatics might fall over a lot. Or hit their head against a wall.
Unfortunately Redgrave provided no drawings of his safety cap.

Posted By: Alex - Thu Nov 04, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Inventions, Patents, Headgear, Nineteenth Century
Device to prevent mouth breathing
In 1920, Richard Jefferies was granted a patent for "a simple and practical device which will eliminate the habit of breathing through the mouth and at the same time will assist in harmonizing the facial features of the wearer, by more evenly balancing the muscles of expression."His invention consisted of a piece of adhesive-backed silk placed over the mouth.
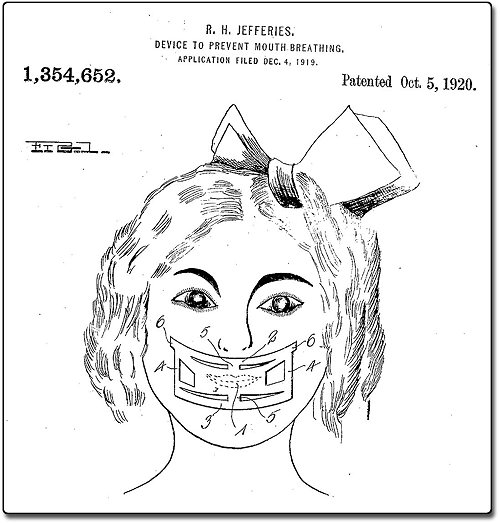
I was vaguely aware that mouth breathing is considered a bad habit, but I wasn't aware that "mouth taping" continues to be a common remedy for it.
For instance, one can buy SomniFix Sleep Strips, which look like they're a slightly updated version of Jefferies' invention.

Posted By: Alex - Wed Oct 27, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Health, Inventions, Patents, 1920s, Face and Facial Expressions
Alfred Schmitz’s Casket with Internal Body Supports
A casket designed for upright burial. From Schmitz's 1975 patent:In the past, caskets and vaults have been buried in a substantially horizontal position. Burial space, especially in urban areas, is becoming more scarce. A solution to such a problem may be found in burying caskets in a substantially vertical position. With such burial techniques, the amount of space required for each burial is substantially reduced.
While previously known caskets could be buried vertically, rather than horizontally, it should be realized that their use might be found distasteful by those who have been close to the party to be buried. An objection to the use of prior caskets may be found in the fact that in prior caskets generally there is nothing to support the body against shifting toward the foot end of the casket when buried in an upright position. Thus, if a conventional casket is tipped upright the body would slump to the foot end of the casket.
Related post: Upright Burial

Posted By: Alex - Thu Oct 21, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Death, Inventions, Patents, 1970s
Scott Perky’s Bi-Directional Text
Henry Perky invented shredded wheat. His son, Scott, was also an inventor, though not as famous. He invented and patented a bi-directional, symmetrical font which could be read from left-to-right or right-to-left.
Perky's idea was that this would allow one to read a line of text from left to right, and then read the next line right to left, without having to move the eye back to the beginning of the line. This, he claimed, would reduce "brain fag":
It is hardly necessary to allude to the strain upon the eyes and brain, which results from much reading. To students, researchers and others whose lives are cast among books, any device which promises to facilitate reading in such wise as to lessen fatigue of the optical tract, and consequent headache and brain fag, will appear of unusual importance.
Randy Ludacer of Beach Packaging Design took the time to set the first three lines of Perky's patent in the bi-directional font, so you can experience what it would be like to read it:
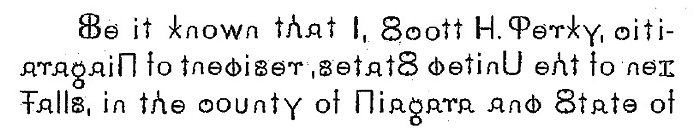
Posted By: Alex - Fri Oct 08, 2021 -
Comments (5)
Category: Inventions, Patents, Languages, 1900s

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




