Philosophy
The Idea
Posted By: Paul - Sun Sep 08, 2024 -
Comments (0)
Category: Philosophy, Allegories, Parables, Fables and Moral Lessons, Cartoons, 1930s
Life Is Flashing Before Your Eyes
Posted By: Paul - Sun May 19, 2024 -
Comments (0)
Category: Music, Philosophy, Surrealism, Cartoons, Psychedelic, 1980s
Infinite Conversation
infiniteconversation.com
Posted By: Alex - Fri Nov 04, 2022 -
Comments (2)
Category: Philosophy, Strange Websites
Existential Tattoos
I think that in the 1950s anything slightly non-conformist was labelled 'existentialist'.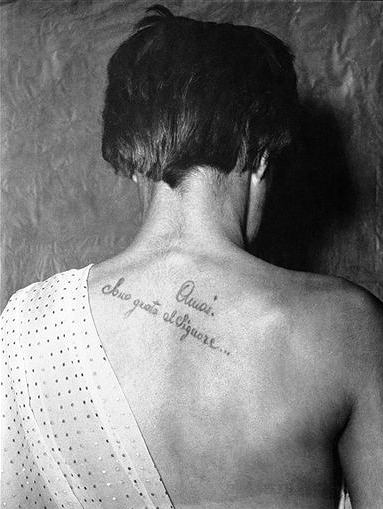

Wichita Eagle - Oct 27, 1952
Anyone with an existential tattoo should make sure to also wear an existentialist hat.
Posted By: Alex - Tue Mar 08, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Fashion, Philosophy, 1950s, Tattoos
Miss Vice
In 1950, while Americans were bestowing titles such as 'Miss Potato Chip' or 'Miss Typical Teen' on young women, the French elected a 'Miss Vice'.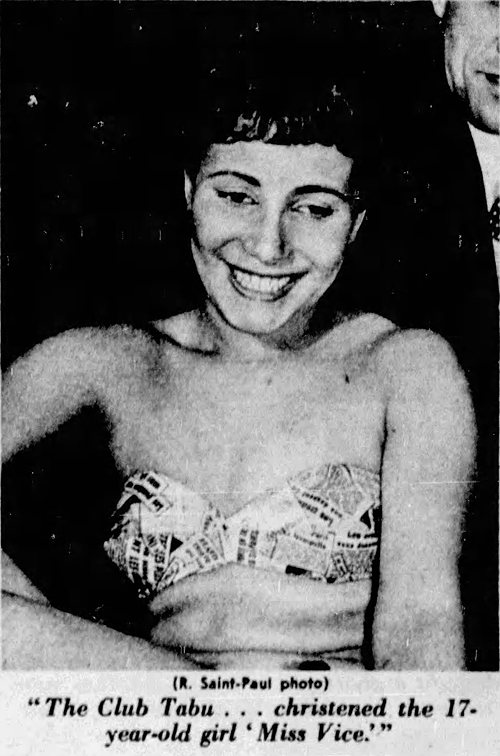
Chicago Tribune - July 3, 1950
The winner was 17-year-old Diane Erdos. Some details from the NY Daily News (Jun 25, 1950):
The sexy brunette showed up with a costume made of three rather small pieces of newspaper — and won hands down over eight other contestants. The selection was popular. The crowd in the smoke-filled Cave Tabou congratulated Diane so enthusiastically that she lost her clippings and was carried unadorned on the shoulders of her admirers until the cops rescued her with a voluminous cape.
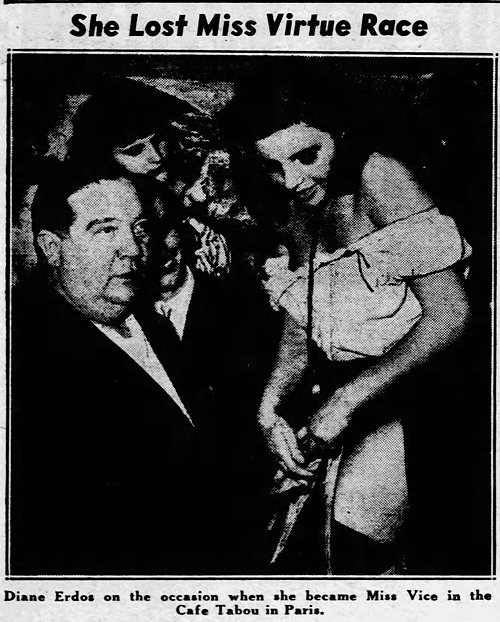

NY Daily News - June 25, 1950
Miss Vice, who was the daughter of a wealthy industrialist, was soon after arrested for trying to blackmail one of her father's friends, threatening to tell the police that he was trafficking cocaine and illegally exporting ball bearings to countries behind the Iron Curtain.
When arrested, she confessed, saying, "I wanted the money to travel around the country and teach Existentialism to the youth of France. I intended to reveal my body in the interests of this new religion, so the sensation would bring me big audiences of young people to hear about M. Sartre's new philosophy."
Posted By: Alex - Wed Sep 01, 2021 -
Comments (2)
Category: Awards, Prizes, Competitions and Contests, Philosophy, Ethics and Morals, 1950s
Video Village
This is getting meta! A TV game show that uses people as living tokens on a board game set is later replicated as an actual board game. Wow, man!The Wikipedia page.
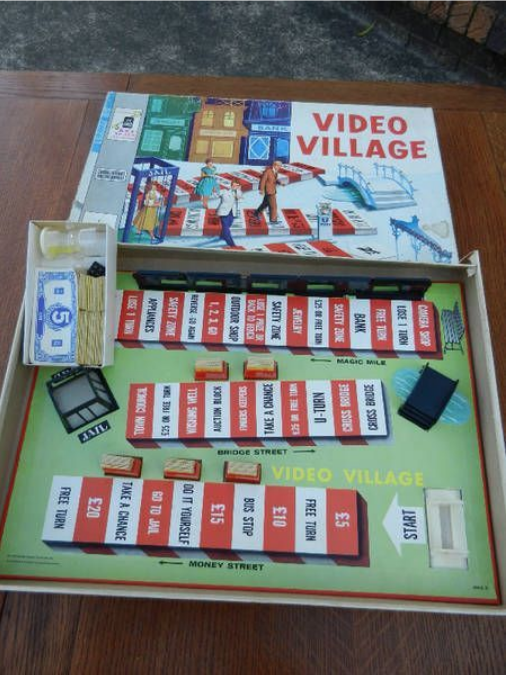

The entry at Board Game Geek.
Posted By: Paul - Mon Jun 28, 2021 -
Comments (2)
Category: Games, Philosophy, Television, 1960s
To Be Alive
Moments of surreal or bizarre imagery in a nice little film about enjoying life.
One weird addendum: you are seeing only one-third of the film. The film was meant to run on three screens simultaneously, with different imagery on each screen, although sometimes, I think, they synchronized.
Posted By: Paul - Sun Nov 15, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: Movies, Documentaries, Philosophy, Surrealism, 1960s
The jokes of Immanuel Kant
We've posted before about jokes from unlikely sources, such as the jokes of Lord Aberdeen, and the jokes of King George VI. Now, along similar lines, comes a book from Robert Clewis — Kant's Humorous Writings . It's a collection of 30 jokes told by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant.
Kant and humor are, I'm guessing, two things most people wouldn't associate together. And after reading Clewis's book, their opinion on this subject may not change.
Clewis freely admits this. In his preface he notes that he was "once tempted to call the book Kant’s Humorous Writings: I Wish They Existed." He goes on to say, "Readers may find the jokes to be boring or even offensive. No promise is being made that the reader will find the jokes amusing."
But Clewis also insists that the book itself isn't a joke. Nor was his intent to lampoon Kant. As he describes it, while studying Kant he realized that the philosopher's work included occasional jokes. His curiosity aroused, he thought it would be interesting to collect these jokes together, as a way of understanding what Kant thought was amusing.
Each joke is accompanied by an illustration drawn by artist Nicholas Ilic. So it's very much a book geared for a general audience. (Admittedly, an audience who appreciates offbeat, erudite material). Personally I think it seems like a great coffee table book. But then, I'm strange that way.
I've reproduced two of Kant's jokes, as well as Clewis's explanation of them, below.
Amazon link
There was once a young merchant who was sailing on his ship from India to Europe. He had his entire fortune on board. Due to a terrible storm, he was forced to throw all of his merchandise overboard. He was so upset that, that very night, his wig turned gray.
Explanation:
This joke comes from the Critique of the Power of Judgment (1790), one of Kant's three Critiques. He contrasts this version with another version: the merchant's hair turns gray. But in that version, we listeners or readers become more concerned and involved. We empathize with the merchant and feel his pain more than in the first version. When it's just a wig, we are in a better position to find the story amusing. We hear the narrative as a joke rather than as descriptive speech, a real story about the world that can be either true or false.
Kant thinks that when we hear or read a joke as a joke, we need to be removed from the situation or story; we cannot have something at stake in it. He calls this disinterestedness, which turns out to be a key principle in his aesthetic theory and account of beauty. "Taste is the faculty for judging an object or a kind of representation through a satisfaction or dissatisfaction without any interest. The object of such a satisfaction is called beautiful." While the humorous is not the same as the beautiful, Kant thinks that our response to both of them requires a kind of disinterestedness. A notion of disinterestedness can be found in the writings of Shaftesbury (Anthony Ashley Cooper) (1651–1713) and other eighteenth-century aesthetic theorists. Today the notion of disinterestedness remains controversial. Some theorists think that the idea can be better captured by the concept of absorbed attention or focus.

Immanuel Kant
A man's rich relative dies. Suddenly he is rich. To honor his relative, the man wants to arrange a solemn funeral service. But he keeps complaining that he can't get it quite right.
"What's the problem?" someone asks.
"I hired these mourners, but the more money I give them to look grieved, the happier they look."
Explanation:
This is a second joke from the Critique of the Power of Judgment. Kant is using it to illustrate his incongruity theory of humor. When we learn that the mourners are happy because they are getting paid, he says, our expectation is suddenly "transformed into nothing."
The philosophical underpinning is that there are at least two levels of satisfaction at work: we feel sadness, joy, etc. (first-order satisfaction) and then can approve or disapprove of it using reason (second-order). A man can be glad that he is receiving an inheritance from a deceased relative, yet disapprove of his gladness. "The object can be pleasant, but the enjoyment of it displeasing."
The joke turns on something similar happening with the mourners. They are so happy that they are getting paid (second-order) that they are no longer able to look sad (first-order).
There is a similar anecdote in Plato's Ion, a dialogue about a professional reciter (a "rhapsode") named Ion, who aimed at moving his audience. Ion says that when he looks out at the audience and sees them weeping, he knows he will laugh because it has made him richer, and that when they laugh, he will be weeping about losing the money.
Posted By: Alex - Mon Sep 28, 2020 -
Comments (2)
Category: Humor, Jokes, Philosophy, Books
Cyriak and Sparks: The Existential Threat
Posted By: Paul - Sat Sep 12, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Death, Destruction, Music, Philosophy, Surrealism, Special Effects
Cosmic Guinea Pig
Posted By: Paul - Sat Mar 14, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Animals, Anthropomorphism, Humor, Philosophy

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




