Pregnancy
The housewife who became pregnant after watching Uri Geller
March 1974: a Swedish housewife claimed that, after she watched Uri Geller on TV, her contraceptive coil got bent out of shape, thereby causing her to become pregnant.Given that the housewife was never named, I'm going to assume this story sprang from the overly fertile imagination of the "Sunday Mirror Reporter in Stockholm".
Uri Geller references the event in his biography, posted on his website, but gives no more details than are available in the Sunday Mirror story, which suggests that, at the very least, he was never sued by the Swedish housewife.

Sunday London Mirror - Mar 17, 1974
Posted By: Alex - Sun Apr 10, 2022 -
Comments (2)
Category: Paranormal, 1970s, Pregnancy
How the Virgin Mary got pregnant
According to ancient Christian tradition, it was through her ear. Details from JohnSanidopoulos.com: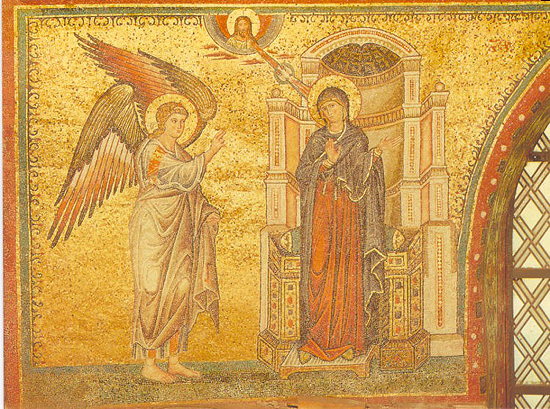
Posted By: Alex - Wed Mar 30, 2022 -
Comments (4)
Category: Religion, Pregnancy
Follies of the Madmen #524
Posted By: Paul - Thu Jan 27, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Robots, Technology, Advertising, Cats, Asia, Pregnancy
The Sins of the Children

Article source.
WASHINGTON POST coverage here.
Here is the official write-up of the case and its outcome.
Posted By: Paul - Wed Jan 13, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Lawsuits, Parents, Teenagers, 1990s, Pregnancy
Fetal Paperweight

Source.
Posted By: Paul - Tue Feb 04, 2020 -
Comments (2)
Category: Body, Pregnancy, Business, Advertising
Human-Animal Breastfeeding
In his 1826 book A Treatise on the Physical and Medical Treatment of Children, the American physician William Potts Dewees offered this advice for pregnant women:
The Wikipedia article Human-animal breastfeeding offers some background info:
English and German physicians between the 16th and 18th centuries recommended using puppies to "draw" the mother's breasts, and in 1799 the German Friedrich Benjamin Osiander reported that in Göttingen women suckled young dogs to dislodge nodules from their breasts. An example of the practice being used for health reasons comes from late 18th century England. When the writer Mary Wollstonecraft was dying of puerperal fever following the birth of her second daughter, the doctor ordered that puppies be applied to her breasts to draw off the milk, possibly with the intention of helping her womb to contract to expel the infected placenta that was slowly poisoning her.
Animals have widely been used to toughen the nipples and maintain the mother's milk supply. In Persia and Turkey puppies were used for this purpose. The same method was practised in the United States in the early 19th century; William Potts Dewees recommended in 1825 that from the eighth month of pregnancy, expectant mothers should regularly use a puppy to harden the nipples, improve breast secretion and prevent inflammation of the breasts. The practice seems to have fallen out of favour by 1847, as Dewees suggested using a nurse or some other skilled person to carry out this task rather than an animal.
Posted By: Alex - Sat Jan 18, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Animals, Medicine, Nineteenth Century, Pregnancy
Girl Scouts File Suit
The most controversial poster of 1969, which prompted the Girl Scouts to file suit. Although a judge threw out the case, citing no evidence that the organization had suffered any damages.Read the lawsuit: GIRL SCOUTS OF U.S. OF A. v. PERSONALITY POSTERS MFG. CO.

source: Vintage Girl Scout

Clarksville Leaf-Chronicle - Aug 6, 1969

Austin American - Oct 10, 1969
Posted By: Alex - Tue Oct 09, 2018 -
Comments (6)
Category: Lawsuits, 1960s, Pregnancy
Lactagol
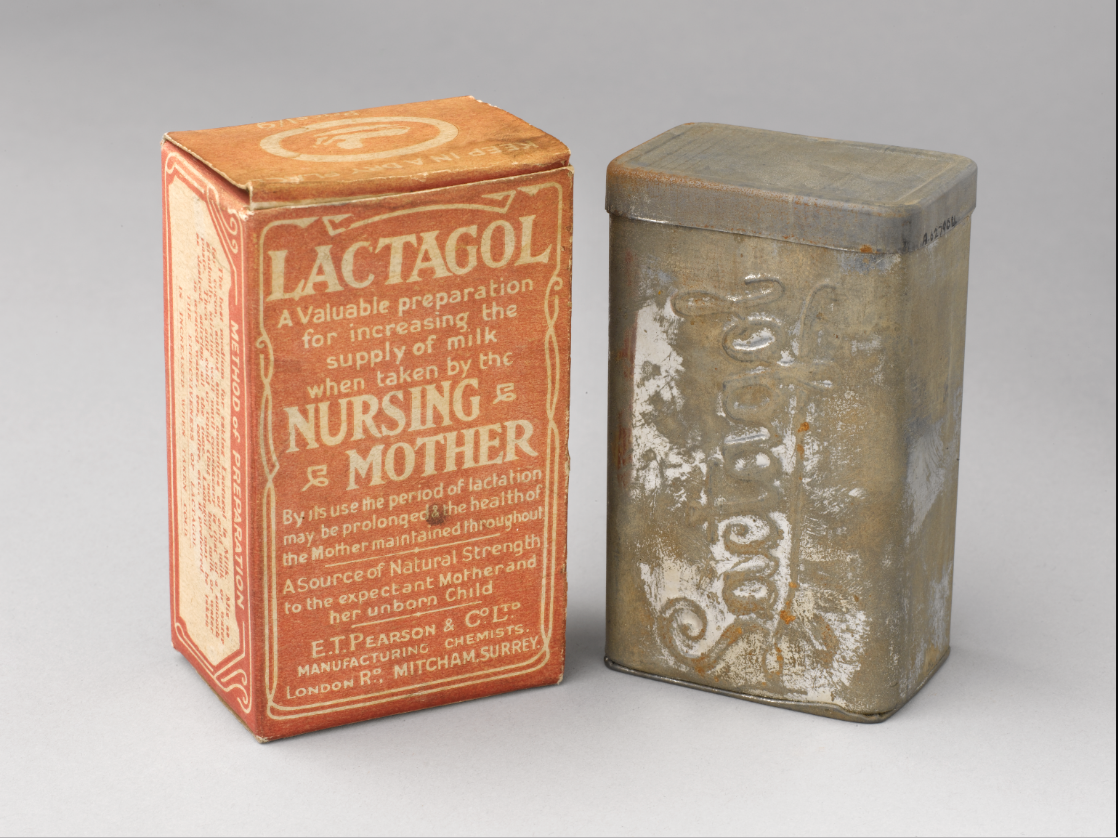
Source.
So far as I can tell, cottonseed of any variety does not promote breast milk production. Flaxseed however is another thing.


Posted By: Paul - Thu Sep 13, 2018 -
Comments (1)
Category: Body, Pregnancy, Patent Medicines, Nostrums and Snake Oil, Babies and Toddlers, Nineteenth Century
Her Own Midwife

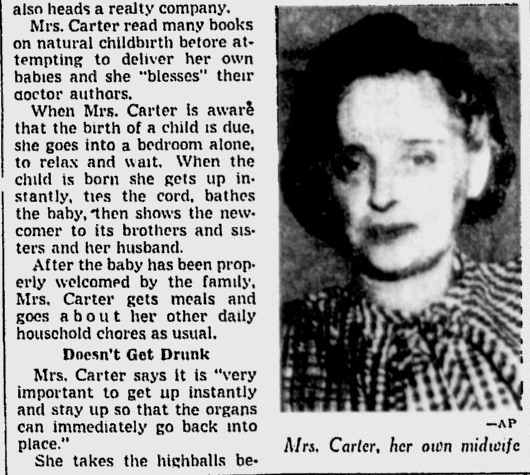
Source.
Posted By: Paul - Thu Aug 09, 2018 -
Comments (1)
Category: Daredevils, Stuntpeople and Thrillseekers, Babies and Toddlers, 1950s, Pregnancy, Alcohol
Coffin Birth
Also known as "postmortem fetal extrusion." The term describes the phenomenon of a dead woman giving birth to a dead baby, the "birth" being caused by the buildup of gas pressure in her decomposing body. It's not known for sure that this actually happens, because no one has ever witnessed it, but archaeological evidence has led researchers to conclude that it probably does.More info: Bones Don't Lie, Seeker, Wikipedia.

Posted By: Alex - Sat May 06, 2017 -
Comments (2)
Category: Death, Pregnancy

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




