Science
Same color illusion and Space Station
Compliments of one of my favorite sites -- the Astronomy Picture of the DayFirst, a same color illusion (originally from Wikipedia).
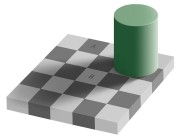
Next is the Space Station.
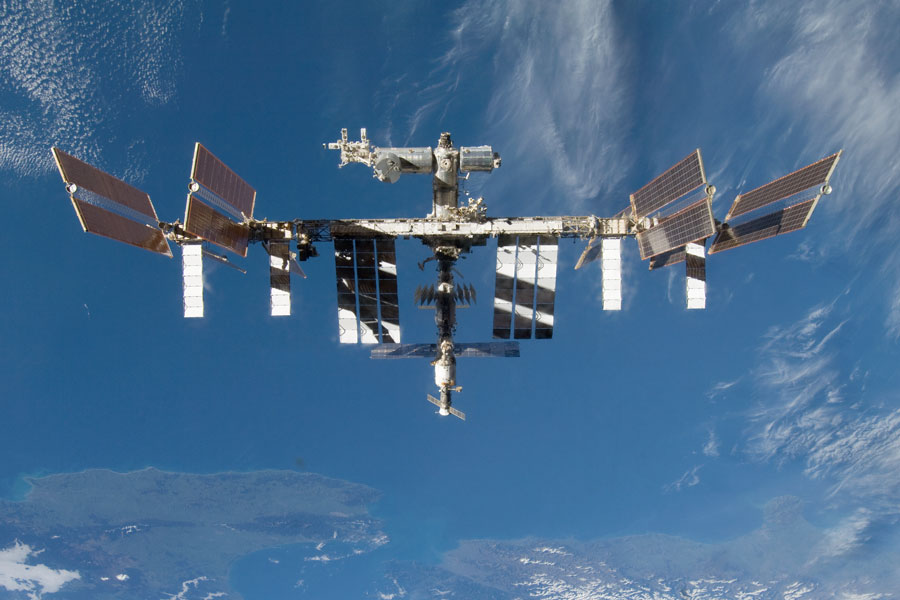

Some other images to check out are the "Old Faithful Full Moon" from October 3rd and the Hologram Tea pot (with a complicated explanation) from September 13th.
This website has lots more than just pictures of the sky!!
Here's the website:
http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/archivepix.html
Posted By: gdanea - Sun Oct 11, 2009 -
Comments (2)
Category: Science
Tectonic plates movement over 650 million years
Cool simulation of past and future tectonic plate movement!!I like the music too!!
Posted By: gdanea - Fri Sep 11, 2009 -
Comments (5)
Category: Science
The Invisible Woman
Anyone ever seen this? It looks like some real dumb fun......
Posted By: Paul - Wed Sep 09, 2009 -
Comments (5)
Category: Movies, Science, 1940s, Women
Weird Science - Heavens Above!

Closer to home, relatively, is the planet is known only as WASP-18b, but if it were ever to be given a proper name it would be “Icarus”, for this is a planet that has flown too close to its sun. WASP-18b is the 375th extrasolar planet discovered by astronomers, and is possibly the most extreme one yet. It is another gas giant like Jupiter, but ten times the size of our neighbourhood giant, yet it orbits its star in less than a day. This 22.5 hour long “year” would mean the planet is so close to its sun, and moving so fast, that tidal forces are almost certainly dragging the planet inwards to its doom. The team from Keele University that discovered WASP-18b, led by Coel Hellier, calculate that realistically the planet probably has less than a million years left (Nature).
More in extended >>
Posted By: Dumbfounded - Thu Aug 27, 2009 -
Comments (8)
Category: Aliens, Armageddon and Apocalypses, Art, Science
A Little Light Weirdness - 5

Or perhaps this is simply proof that Scottish universities have got the jump on their transatlantic counterparts? In a move nearly, but not quite, totally unlike Jurassic Park, Professor Hans Larsson of McGill University in Montreal has announced that he hopes to de-evolve chickens back into their dinosaur ancestors. Larsson stressed that he is not aiming to recreate whole dinosaurs at this time, but by switching on or off certain genes in chick embryos he hopes to induce atavistic dinosaur anatomy in the full grown animals (AFP).
More in extended >>
Posted By: Dumbfounded - Wed Aug 26, 2009 -
Comments (12)
Category: Animals, Ceremonies, Weddings, Contests, Races and Other Competitions, Cryptozoology, Fictional Monsters, Fairs, Amusement Parks, and Resorts, Geography and Maps, Inebriation and Intoxicants, Nature, Science, Experiments, Surrealism
I’ll Huff And I’ll Puff…
From the BBC children's science show "Bang Goes The Theory...", engineer Jem Stansfield builds himself a giant vortex cannon, and tries to knock down buildings made of straw, wood and bricks...Impressive, though I'm sure the "Big Bad Wolf" would not have had much of a problem if the third little pig had likewise left out the mortar. Mind you, one of these is just what I need to keep the neighborhood cats out of my garden! :cheese:
Posted By: Dumbfounded - Tue Aug 18, 2009 -
Comments (7)
Category: Buildings and Other Structures, Destruction, Geeks, Nerds and Pointdexters, Guns, Inventions, Science, Experiments, Television, Myths and Fairytales
A Is For Atom
Posted By: Paul - Wed Aug 12, 2009 -
Comments (2)
Category: Destruction, Science, Documentaries, 1950s
The Great Wall of Africa?
Problem: Desertification (when viable land is encroached upon by desert) threatens the lives of millions of people in Africa. Solution: Build a wall to keep the desert from spreading. According to architect Magnus Larson, it is not as difficult as you might imagine. Take sand dunes at the edge of the desert, combine them with a mixture of water and bacteria, let dry and you've got an instant sandstone wall! Read all about it at BBC news.
Posted By: fyshstyxx - Tue Jul 28, 2009 -
Comments (5)
Category: Architecture, Disasters, Science, Africa
So Weird It Hurts?
Cartoon expletives aside, a bit of invective can do you the world of good, or so said scientists recently. A research team from from Keele University asked volunteers to hold their hand in freezing water for as long as they could manage while repeating either an innocuous word or the swear-word of their choice. The swearers held out for an average of two minutes, while non-swearers managed only 1 minute 15 seconds. But while Rohan Byrt of the Casual Swearing Appreciation Society claimed the study demonstrated the benefits of swearing, team leader Richard Stephens warned that everyday swearing would lessen its painkilling effects. "Swearing is emotional language" he explained, "but if you overuse it, it loses its emotional attachment" (BBC News).
From this week, pregnant women throughout Britain considering "letting it out" to help with the pain might also want to direct their curses towards Dr Denis Walsh, associate professor of midwifery at Nottingham University in England. In an article in the journal Evidence Based Midwifery, Dr Walsh claimed last week that the pain of childbirth was useful and a "timeless rite of passage", and women should not be trying to avoid it with epidural anaesthesia. Walsh based his statement on the fact that the use of epidurals has almost doubled in the past two decades, claiming that in 20% of cases, the procedure was unnecessary. While some, like Dr. Justin Clarke of the Birmingham Women's Hospital, rejected Walsh's data, saying it was wrong to characterise modern women as "less stoical", others supported him, such as Mary Newburn of the National Childbirth Trust who spoke of there being an "epidural culture" (Telegraph).
But perhaps women might be convinced to trade in the needle for a fancy rubber suit? Baltimore company Under Armour has developed a hi-tech, full length bodysuit that is said to allow athletes recover more quickly after strenuous activity. Under Armour's "Recharge" range gently squeezes the athlete's body forcing excess fluid out of the muscles and back into the bloodstream over a period of hours after a workout, reversing the "pumped" effect of the exercise. Research by the University of Connecticut showed that doing so resulted in subjects feeling less soreness and swelling of the muscles and recuperating faster (Journal Gazette).
More in extended >>
Posted By: Dumbfounded - Tue Jul 14, 2009 -
Comments (3)
Category: Exercise and Fitness, Frauds, Cons and Scams, Health, Injuries, Medicine, Obscenity, Science, Experiments, Stupid Criminals, Weddings
Weird Science - Biology
Men are now obsolete, thanks to work by scientists at the Northeast England Stem Cell Institute. Professor Karim Nayernia and team have managed a "scientific first" by inducing stem cells into becoming artificial sperm in laboratory conditions. In mice, these sperm have proven able to fertilise eggs and produce viable offspring, opening the door to potential new infertility treatments in humans. Additionally, the stem cells themselves may come from either sex, raising the possibility of children being born without the traditional male input. Any such treatment is many years away however, and there are still problems to be overcome, not least that all the mice babies so far produced by this technique had abnormally short lives. Nayernia admits that the process is not perfect, but says that it could be ready for human trials in less than ten years (Telegraph).But mothers, don't kick out the old man yet, not if you want a little help with the childcare that is. A team from the "Institut des Sciences de l'Evolution" in France has confirmed a prediction of the theory of evolution that fathers will invest more in children that resemble them. A total of 30 Senegalese families were studied and the paternal investment and resemblance were quantified for each. As expected, there was a significant correlation between the resemblance and investment scores, but also between investment and the nutrition and health of the child. So it seems we fathers still have our uses, for now (Science Daily).
Animals do many weird things to avoid being eaten, from camouflage, to making themselves look bigger or more dangerous, to having a false head or eye on a less vital point to divert attackers. However, one spider has a tactic that's never been observed before; it makes decoy models of itself. The Cyclosa mulmeinensis spider of Orchid Island, near Taiwan, decorates its web with pellets of silk the same size and (to wasps) colour as itself, then hides among them. Researchers from Tunghai University were actually able to observe wasp predators attacking the decoys while the spider escaped, confirming the effectiveness of the trick. The strategy is not without risk though, by having more spider sized blobs on it, the web may also be easier for the wasps to detect (Daily Mail).
More in extended >>
Posted By: Dumbfounded - Wed Jul 08, 2009 -
Comments (6)
Category: Animals, Babies, Family, Insects and Spiders, Medicine, Science, Anthropology

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




