Science
Black Hole Symphony
Black Hole Symphony, which was penned by composer David Ibbett and is due to be performed by an orchestra at the Museum of Science in Boston, Massachusetts, blends real science into the creative mix.
The work cleverly translates cutting-edge research on black holes into an electro-symphonic score with five movements and includes visuals based on images taken by scientific instruments, including the Event Horizon Telescope, a large array made from a global network of radio telescopes, which took the first image of a black hole.
Not to be confused with "Black Hole Sun."
Posted By: Paul - Thu Jul 21, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Music, Science, Spaceflight, Astronautics, and Astronomy, Cacophony, Dissonance, White Noise and Other Sonic Assaults
The Dinosaur and the Missing Link
Posted By: Paul - Mon Jun 13, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: History, Unexplained Historical Enigmas, Movies, Science, Dinosaurs and Other Extinct Creatures, 1910s
Anthropometry of Airline Stewardesses
The research study "Anthropometry of Airline Stewardesses" consists of detailed body measurements of 423 stewardess trainees. It was paid for by the FAA and released in March 1975. The trainees were from the American Airlines Stewardess Training Academy in Fort Worth, Texas.The justification for the study was that knowing the body measurements of stewardesses might help engineers design better seats and safety equipment for them. But what the study really seems to demonstrate is that in the early 1970s airline stewards were expected to be young, thin, female, and single. None were older than 28. None weighed more than 145 lb. Only 26 were divorced. The rest had never been married.
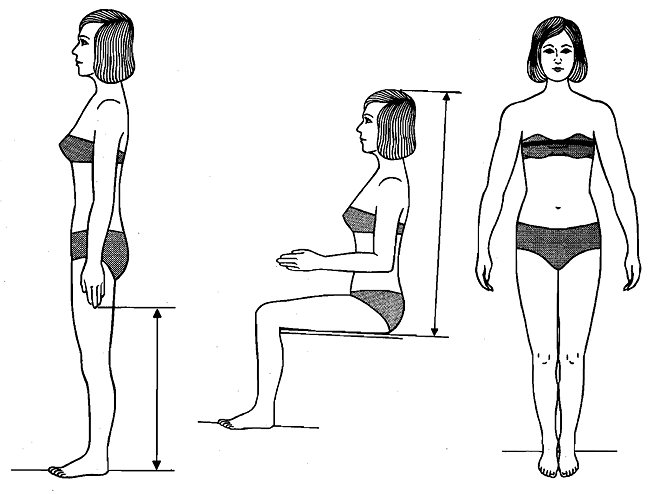
The study attracted the scorn of Senator William Proxmire. Details from a Reuters article in The Calgary Herald (Aug 21, 1975):
Senator William Proxmire says the disclosures neither enlighten nor amuse him.
The Wisconsin Democrat said today the report, with detailed measurements on 423 stewardess trainees for American Airlines, was another case of taxpayers' money spent on discovering the obvious. "It seems like a bust to me," he said...
Seventy-nine individual body measurements were taken as part of the study, and some, the senator said, seemed unnecessary or irrelevant.
"Detailed measurements were made of body features such as the skinfold of the upper arm and the posterior calf, the vertical height of the sphyrion, the popliteal length of the buttocks, the transverse distance between the centres of the anterior superior iliac spines, the knee-to-knee breadth while sitting, the maximum horizontal width of the jaw across the gonial angles, and the height of the nose," he said.
There were too many deviations among even general measurements of young trainees to help designers of airline equipment, he argued.
Their weights ranged from 94 to 145 pounds, heights from five feet one inch to six feet one inch, busts from 29 to 37.5 inches and waists from 21 to 28 inches.
The senator concluded: "About all that can be said to aircraft designers is that stewardesses are young women with the body measurements of young women."
Posted By: Alex - Mon May 30, 2022 -
Comments (5)
Category: Body, Science, Air Travel and Airlines, 1970s
The Pressed Frog Phenomenon
I found the image below at the Texas History site of the University of North Texas. It appears there as is, without any further explanation (or date).
I realize that the indentations on top of bricks are called 'frogs', but why were actual frogs being placed inside bricks?
As far as I can tell, it must have been an experimental demonstration of the 'pressed frog phenomenon' — this phenomenon being that one can place a living frog inside a brick as its being made, apply thousands of pounds of pressure to the brick to mold it, and the frog will survive. The frog won't be happy about the experience, but it won't burst. Whereas the same pressure applied to a frog that isn't in a brick will definitely cause it to burst.
Obviously the brick hasn't been heated in a kiln, because that would definitely cook the frog.
The article below from 1925 explains the science of why a frog in a brick doesn't burst. The key part of the (overly long) explanation is this sentence:
However, this doesn't solve the mystery of who first decided to put a frog in a brick.


Clarion Ledger Sun - Aug 16, 1925
Posted By: Alex - Mon May 23, 2022 -
Comments (5)
Category: Animals, Science, Experiments, 1920s
Knives made from frozen human feces
The non-fiction book Shadows in the Sun by Wade Davis contains the following passage:This caught the attention of some archaeologists who decided to test if a knife made from human feces would actually be strong enough to cut through muscle and tendons. They published their results in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
The researchers paid close attention to detail. For instance:
However, the results were disappointing: "the knife-edge simply melted upon contact, leaving streaks of fecal matter."
Conclusion: the story of the fecal knife was an urban legend.
Posted By: Alex - Fri Mar 25, 2022 -
Comments (4)
Category: Science, Experiments, Excrement
Mystery Gadget 100
What's happening with these poor doggos?The answer is here.
Or after the jump.
More in extended >>
Posted By: Paul - Fri Feb 11, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Science, Dogs, 1930s
The Mentality of the Criminal Woman
Read it here.
The majority of the book consists of dry statistical tables and charts of the tests given to the subjects.

But in the latter third of the study, conclusions begin to be drawn.

Posted By: Paul - Thu Jan 13, 2022 -
Comments (1)
Category: Science, Studies, Reports, White Papers, Investigations, 1910s, Women
Formaldehyde Hunger
According to medical student lore, the smell of formaldehyde while dissecting bodies stimulates the appetite. This phenomenon is known as 'formaldehyde hunger'.It was mentioned in a 2020 article by Amalia Namath in the Georgetown Medical Review, and that's the earliest reference to it I've been able to find:
An article on mashed.com disputes the reality of the phenomenon, noting, "there is some self-reported evidence of formaldehyde actually having the opposite effect — constricting hunger, rather than inducing it."
My guess is that med students just naturally build up an appetite during the long hours they're dissecting a cadaver. After all, they're presumably not snacking while they're doing this. The formaldehyde has nothing to do with their hunger. But it makes a better story to attribute their food cravings to the formaldehyde.
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jan 09, 2022 -
Comments (1)
Category: Food, Science, Fables, Myths, Urban Legends, Rumors, Water-Cooler Lore
Urohidrosis
Back in the 1960s, while observing wood storks in Florida, biologist M. Philip Kahl, Jr. noted that on hot days the storks "have the unusual habit of frequently excreting on their legs."He eventually concluded that, since storks don't sweat, they were doing this to cool themselves down "by means of evaporative cooling of the blood supply to the legs and feet." He named this phenomenon 'urohidrosis'.
His hypothesis is now accepted as true, and it's not only storks that cool themselves by pooping on their legs. Turkey vultures do it too.
Reference: Kahl, P.M., Jr. 1963. Thermoregulation in the Wood Stork, with special reference to the role of the legs. Physiol. Zool., 36: 141-151.
Posted By: Alex - Tue Dec 14, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Animals, Science, Excrement
Hand-Sniffing After Handshakes
Research by biologists Noam Sobel and Idan Frumin reveals that after a handshake people frequently lift their hand to their nose and sniff it. The researchers hypothesize that this is to smell the body odor of the other person.As described by Sarah Everts in her recent book The Joy of Sweat:
"When we showed them the videos, many of the subjects were completely shocked and disbelieving," Frumin told me. "Some thought we had doctored the videos - not that we had the computing power or the expertise to do so."
. . . When Frumin now goes to conferences, he sometimes stands back and watches people unconsciously sniffing. "Sometimes I catch myself doing it too. People tell me I've ruined handshakes for them, that they've become very self-conscious about shaking hands, especially with me."
The Weizmann Institute has more info. Sobel and Frumin's article about their research is in the journal eLife Sciences.
Posted By: Alex - Wed Dec 08, 2021 -
Comments (6)
Category: Science, Experiments, Smells and Odors

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




