Science
American Tentative Society
The officers of the American Tentative Society insisted that, despite the odd name, the society wasn't a joke. Its purpose, they explained, was to promote the idea that scientific knowledge should always be regarded as tentative — subject to growth, revision, and change.The three founders of the society were science journalists Alton Blakeslee, Rennie Taylor, and Pat McGrady. They came up with the concept in the mid-1960s, but it remained nothing more than a crazy idea until 1974, when Taylor died. In his will he bequeathed $300,000 to making the society a reality. This left the other two stuck with the problem of how to spend the money. So they solicited ideas from the public.
As far as I can tell, they ended up using some of the money to give awards to scientists (such as Stephen Jay Gould) whom they viewed as embracing the tentative nature of scientific knowledge. The rest of it was eventually given to the Council for the Advancement of Science Writing to endow a fellowship awarded annually to students accepted for enrollment in graduate-level programs in science writing.

Posted By: Alex - Tue Oct 19, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Clubs, Fraternities and Other Self-selecting Organizations, Science, 1970s
Crook, the Unkissed
Algie R. Crook (or "Alja" Crook, as his name was sometimes spelled) was a professor of mineralogy at Chicago's Northwestern University. His great claim to fame, however, had nothing to do with science. Instead, it was that in April, 1901 he allegedly told his undergraduate class that he had never kissed a woman. More specifically, he reportedly said, "I have never uttered a profane word, never have smoked or chewed tobacco, drank intoxicants, nor hugged or kissed a woman."Given that he was thirty-seven years old at the time, this was considered a remarkable admission. So remarkable that when word of it leaked to the press it became international news.

Great Falls Tribune - May 15, 1901
The media started referring to him as "Crook, The Unkissed." Acquaintances of Crook (or people who claimed to be his acquaintances) readily confirmed the tale, attributing his lack of kisses to his embrace of "austere science." One said, "the scientific atmosphere is inimical to the love germ."
Offers of marriage flooded in, from women hoping to be the one to thaw the professor's icy reserve.

Philadelphia Times - Apr 28, 1901
The French were particularly taken with the story. As reported in the Leavenworth Times (May 8, 1901):
Supposedly the news even reached as far as China where the dowager empress expressed a desire to see him.

Philadelphia Inquirer - Apr 27, 1901
Crook, for his part, was said to be "abashed and humiliated over the gossip the affair has provoked," and also furious at the "tattling undergraduates."
He issued a denial of the allegation, stating, "I have never told any one that I have refrained from hugging or kissing women, for the reason that I consider it nobody's business but my own."
He recalled having advised a student to do as he did — never to kiss, hug, swear, and so forth. And he figured that's how the story must have started. But he insisted that he hadn't said that he had never done these things at all.
However, it was too late. The story was out there and couldn't be taken back. His denial got buried in the back pages of newspapers, if it was printed at all.
In other interviews, Crook asserted that he had kissed female family members, which didn't help his case much since it implied that he had indeed never romantically kissed a woman. Also, a former student recalled that Crook had made similar claims before, noting, "He is a consistent Methodist, and his convictions sometimes cause him some trouble." So I kind of suspect that Crook really did make the no-kissing claim to his class, but denied it later out of embarrassment.
Whatever the case may have been, the tale continued to haunt him. The following year (1902) a group of students at Northwestern formed an "Anti-osculation Society," claiming that they were "following the teachings of Professor Algie R. Crook, the man who never was kissed." They elected him an honorary member.
In 1904 Crook got married, and inevitably this triggered a renewal of the no-kissing story. "Unkissed Man To Wed," reported the papers.

The Hutchinson News - Dec 28, 1904
Crook and his wife eventually had five children together. He died in 1930, at the age of sixty-six, and the kissing story resurfaced in his Chicago Tribune obituary (June 1, 1930). It was, after all, the achievement he was most famous for:
However, the memorial of him in the Journal of the Mineralogical Society of America omitted the kissing story. Nor is it mentioned on the wikipedia page about him.
Posted By: Alex - Fri Oct 08, 2021 -
Comments (6)
Category: Eccentrics, Science, 1900s, Love & Romance
Fanta Pomelo Ad and Sequel
Posted By: Paul - Tue Sep 21, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Aliens, Humor, Science, Advertising, Twenty-first Century
Aluminum Al
In 1952, scientists at the General Electric Research Laboratory in Schenectady created the aluminum version of a Chia Pet. They called him "Aluminum Al".Source: Google Arts and Culture

Posted By: Alex - Mon Sep 13, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Science, 1950s, Hair and Hairstyling
Butt Breathing Tubes
Recent studies suggest that it may be possible to supply oxygen to patients via a "butt breathing tube" rather than by the traditional tube down the throat. This new technique is also known as "enteral ventilation via anus". Caleb Kelly, in the journal Med (Jun 11, 2021) notes:The key to the technique is the use of an oxygen-saturated perfluorocarbon solution that can deliver enough oxygen to make it through the mucus membrane of the intestines and into the blood.
The technique has been demonstrated successfully on mice, rats, and pigs, but not yet on humans.
Josh Bloom, on the American Council of Science and Health site, observes:
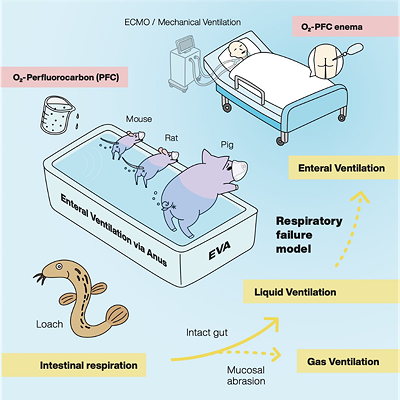
image source: The Scientist
Posted By: Alex - Sat Sep 04, 2021 -
Comments (2)
Category: Science, Experiments
The Penile Plethysmograph
I had to post this item today, to accompany Alex's "pot-sex" post, only because how often does one get to use the great word "plethysmograph?"
Posted By: Paul - Sat Jul 31, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Medicine, Science, Sexuality, Technology, Genitals
International Stop Continental Drift Society
The International Stop Continental Drift Society (ISCDS) was founded in 1976 by geologist John Holden with these demands: "the continents to stop moving, the sea floor to stop spreading, and such inconveniences as major earthquakes and volcanic eruptions to cease immediately." Its motto was "Eschew Sea-Floor Spreading." It also issued a newsletter that "like natural disasters will appear without warning".By 1981 it had grown to 300 members. Mostly fellow geologists. However, Holden admitted, "So far, our demands have not been satisfactorily met."
By the mid-1980s it seems to have faded away. Although it does have a Facebook page (set to private) with 154 members.
More info: Science Year 1982, lgvweb.nl
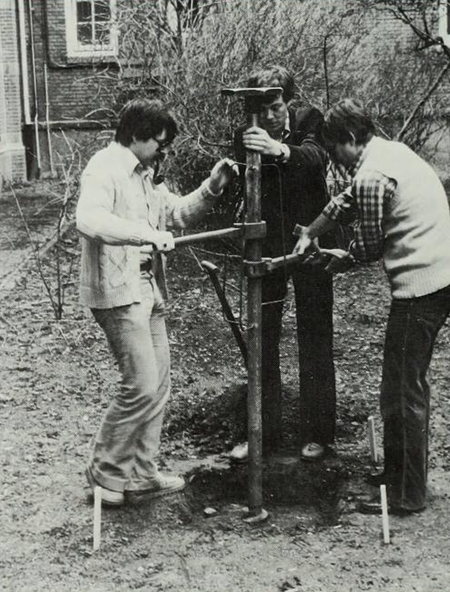


"Dutch geologists drive a giant screw into the ground at Leiden, The Netherlands, in an attempt to stop the Eurasian tectonic plate from moving. The scientists are members of the International Stop Continental Drift Society whose purpose is to put some stability in the earth's crust."
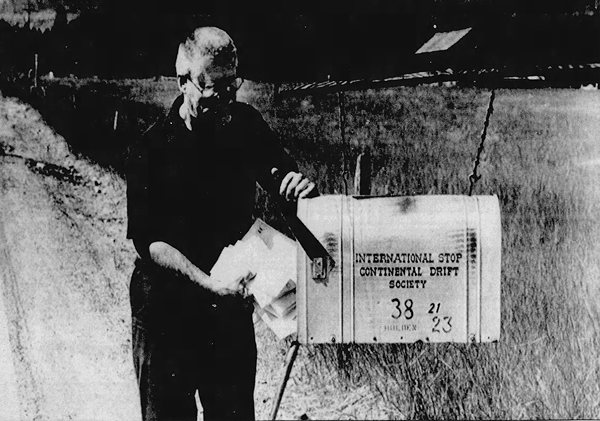

Jack Holden - founder of the ISCDS
Longview Daily News - Sep 15, 1981
Posted By: Alex - Sat Jul 03, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Clubs, Fraternities and Other Self-selecting Organizations, Humor, Science
Whole-Mouse Homogenizer
This scientific ad has been doing the rounds for a long time. (Dave Barry discussed it in a 1993 column). But I only found out about it recently.No idea what the original source was.
via Improbable.com

Posted By: Alex - Sun May 16, 2021 -
Comments (9)
Category: Science, Advertising
Why the man of the future may have only one eye
1927: Scientist W.E. Bailey predicted that, in the far future, our descendants may have only "one large, central, cyclopean eye".Of course, who knows what humans may look like in a million years (if there are even any of us still around), but his argument sounds plausible enough to me (with my limited knowledge of neuroscience). Basically he argued that, over the past several million years, our brains have devoted more space to speech, and less to vision. Extrapolating that trend into the future, he concluded that the eventual merging of our eyes into one would be a more efficient use of the brain's resources, and so will probably happen.

Minneapolis Star Tribune - Dec 4, 1927
"Man's field of view," writes Mr. Bailey, "will become smaller and smaller. This, because his need of a wide field is growing less and less. This I say with full realization that we live in an age of automobiles, and that these vehicles render desirable a wide field of view. The automobile is probably a very transitory phenomenon. I even believe that, in the course of countless ages, the two human eyes will come closer together, the bridge of the nose will further diminish and sink (just as the animal snout, in man's line of descent, has been doing for vast aeons of time) and, finally, man's two eyes will again become one—just one large, central, cyclopean eye.
"It is likely that the merely servient (left) eye will shrink away (as the pineal eye has already done) so that the right eye will become the cyclopean. Certain it is that the left eye, even today, is being used less and less continually. Man's binocular and stereoscopic visions are being destroyed. That is the price he pays for his speech center.
"The great cyclopean eye, however, will regain stereoscopic vision by developing two maculae in the one eye, just in the fashion in which many birds have stereoscopic vision in each eye now. Although the field of view will then be narrower than now, the eye will probably be microscopic and telescopic; it will be exceedingly acute for colors, for motion, and for form; and finally, most important of all, it will probably be able to perceive as light many forms of energy which now produce in human eyes no sort or kind of perception.
"Because of the development of a speech center in man, there has come about what is called dominancy and serviency in human eyes, a phenomenon not found in other mammals. This means that, in the human, the brain does most of the seeing through one eye, even when both eyes are open. Dr. Thomas Hall Shastid, ophthalmologist of St. Luke's Hospital, Duluth, has found that from 95 to 100 per cent of the detail of any object comes through the right eye if the person be right-handed; while if the person be left-handed the left eye as a rule, but not always, takes up the major part of the detail. This condition, which he has been unable to observe in any other animal, may eventually result in consequences of vast importance to humanity."

Posted By: Alex - Sat Apr 17, 2021 -
Comments (5)
Category: Science, Anthropology, 1920s, Eyes and Vision
Armpit Reading
Useless Superpower: In the 1970s, Chinese researchers investigated reports of children who had the unusual ability to read with their armpits. The kids supposedly could describe what was written on folded pieces of paper tucked beneath their armpits. And not just their armpits. Some kids could see with their ears, hands, or feet.After careful study, the researchers concluded that, yes, the children did seem to have this ability.

Edmonton Journal - Feb 15, 1980
The researchers published the results of their study in Nature Magazine, which is a Chinese journal not to be confused with the British journal Nature. Thanks to the U.S. military's translation service, you can read these articles in English. They're posted on the website of the Defense Technical Information Center. Here's a sample:
Therefore, other pieces of paper were written on in another room by Shen Hanchang and Zhu Chiayi. The papers were folded twice and squeezed through the shirt from the backs of the subjects and placed under their armpits. The two girls held the sample against them with their hands. Besides the two writers, no one else in the room knew what was written on the paper.
After 2 minutes 40 seconds, Wang Qiang said that she "recognized" it. Everyone told her not to speak but to write it down on the side. She wrote a "3" and also wrote "blue". They opened the paper and found there was a "3 6" written with a blue ball point pen. The "3" and the "6" were separated some distance and thus she had recognized one half.
I jokingly referred to armpit reading as a useless superpower, but the Chinese researchers would disagree. They concluded their study with this remark:
Posted By: Alex - Sat Feb 27, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Forteana, Freaks, Oddities, Quirks of Nature, Human Marvels, Science, Eyes and Vision

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




