Weapons
Weird alien sounds designed to terrify and panic
In 1969, Alfred Mardarello et al. were granted a patent for a "noisemaking device" which could be attached to a missile. When the missile was fired and flying through the air, their gadget would create "weird, alien sounds" intended to terrify the enemy. From their patent:The psychological effects of weird or unexpected noises, which accompany an artillery projectile or missile, have been explored in many ways, prior to this invention, with minimum results. The Germans, in World War II, attached a noise producing device to aerial bombs, somewhat similar in construction to the organ pipe. A high pitched noise was created. This could be used only on large bombs and was too massive for use on artillery projectiles...
The insufficiencies of the prior art are overcome by the noisemaking adapter of the instant invention. The adapter ring is so designed that they attach to an existant missile without requiring modification of said missile. Centrifugal force, as a result of the spinning motion of the missile after being fired, causes the noisemaking arms or fins to extend and to produce weird, alien sounds of such magnitude as to be heard over a substantial area. The psychological effect, to create panic to those in the vicinity, is thus effected.
I have no idea if this patent was ever used in combat. But I don't really understand the point of making something that's already terrifying (a missile) even more terrifying by having it produce weird, alien sounds. Isn't the terror of the missile itself enough?
I guess it was part of the psychological warfare effort during Vietnam. See also Ghost Tape Number Ten.
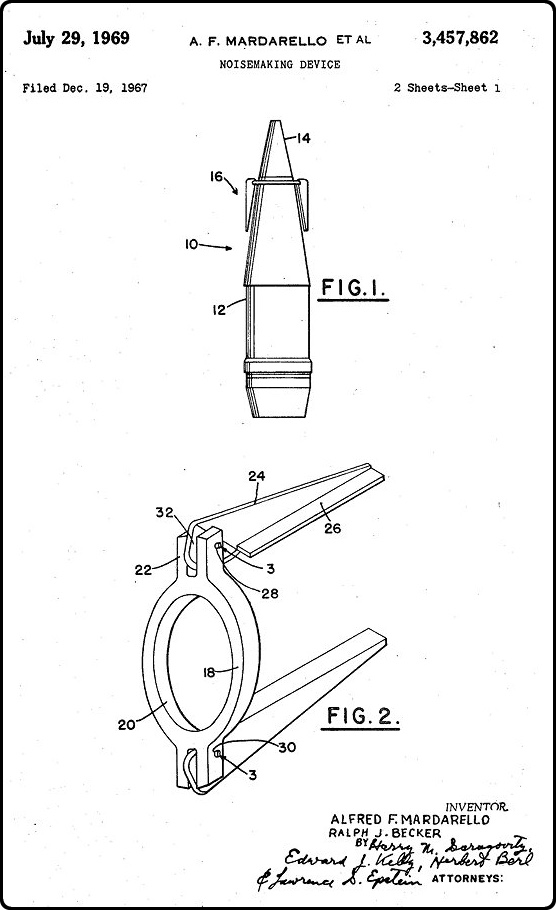
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jul 11, 2021 -
Comments (5)
Category: Patents, 1960s, Weapons, Cacophony, Dissonance, White Noise and Other Sonic Assaults
Horse Spike
In 1899, Patent No. 636,430 was granted to Franz and Konrad Hieke of Philadelphia for what they described as "cavalry equipment". It was essentially a large spike attached to the front of a horse. From their patent:
A better view:

Argos Reflector - Feb 8, 1900
I wonder if one of these was ever actually used in combat?
Posted By: Alex - Tue Jun 22, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Animals, Inventions, Patents, Weapons, Nineteenth Century
The Hand Cannon

Smithsonian article.
Wikipedia page.
Posted By: Paul - Mon Feb 22, 2021 -
Comments (3)
Category: Medieval Era, Renaissance Era, Asia, Europe, Weapons
Grover Loening’s Flying Airstrip

Source.
The inventor's Wikipedia page.
Posted By: Paul - Mon Dec 14, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Excess, Overkill, Hyperbole and Too Much Is Not Enough, War, Weapons, Air Travel and Airlines, 1950s
Ruby Barnett, machine-gun tester
Mrs. Ruby Barnett was one of 1000 women employed at the Aberdeen Proving ground during World War II. Her job there was to test guns, and she attracted quite a bit of media attention because she was a grandmother and didn't exactly look like the kind of person one would expect to see behind a .50 caliber machine gun.Apparently she was only 40, but she already had three grandkids.
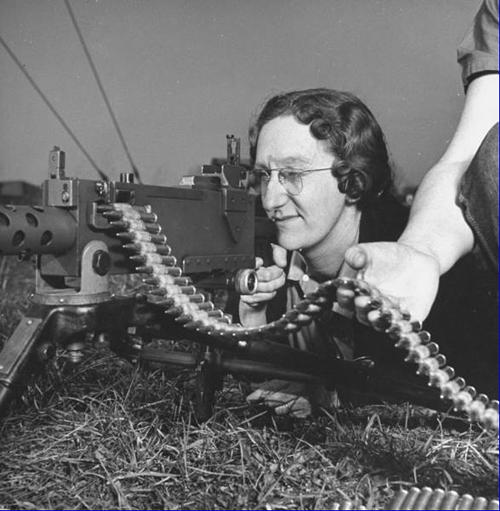

Source: Google Arts & Culture
Mrs. Ruby Barnett, 40, said today as she went about her job of testing all kinds of guns—except 16-inch cannon—that she found nothing inconsistent in gun-firing by day and rocking the cradle of her third and newest grandchild by night.
"Hitler hasn't respected grandmothers or little children in this war and I guess American grandmothers will have to pitch in and fight him any way they can," she said, as she turned from the anti-tank gun, loaded a .50 caliber machine-gun and banged away with nonchalance and a terrific din.
The youthful grandmother, wife of a World War veteran, is employed by the Army, along with 1,000 other women, to test ordnance materiel at the government's oldest and largest proving ground here.
Wilmington Morning News - Oct 2, 1942
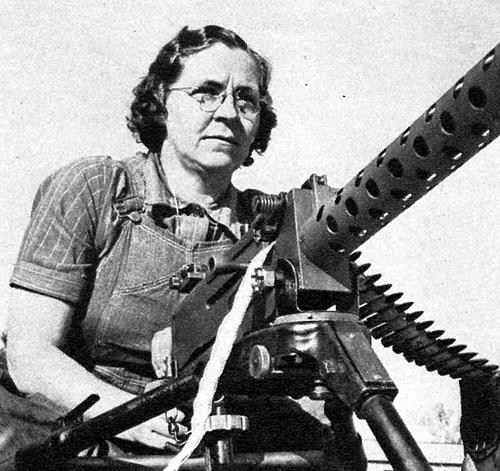

Source: OldMagazineArticles.com

Posted By: Alex - Wed Oct 14, 2020 -
Comments (8)
Category: 1940s, Weapons
Parkinson’s Dream Weapon
How, in 1940, a Bell Labs engineer invented a guidance system for anti-aircraft guns in a dream. Source: The Bigelow SocietyA compelling example in favour of this theory concerns an engineer, David Bigelow Parkinson. The time was spring, 1940 and Parkinson was then a young engineer working at Bell Telephone Laboratories in New York City in the specialized field of electromechanical design. He was working on improving an instrument called an automatic level recorder. A small potentiometer [an instrument for measuring electromotive forces] controlled a pair of magnetic clutches which in turn controlled a pen to plot a logarithm.
Meanwhile, the top story in the headlines concerned the evacuation of hundreds of thousands of stranded Allied soldiers from the beaches of Dunkirk, France across the Channel to England. This news greatly preoccupied Parkinson's mind along with that of his work. And the two ideas came together in a dream, which he later described in an unpublished memoir:
I found myself in a gun pit or revetment with an anti-aircraft gun crew . [A] gun there. was firing occasionally, and the impressive thing was that every shot brought down an airplane! After three or four shots one of the men in the crew smiled at me and beckoned me to come closer to the gun. When I drew near he pointed to the exposed end of the left trunnion. Mounted there was the control potentiometer of my level recorder!
Parkinson realized the full significance of his dream the following morning. If his potentiometer could control the pen on the recorder, something similar could, with the right engineering, control an anti-aircraft gun. At the time, the complex mechanical systems controlling these guns were not very accurate and could not be mass-produced.
Parkinson discussed the idea that morning with his boss, Clarence A. Lovell. They worked for several days writing a report and then met with Lovell's boss. Just before this meeting, on 18 June 1940, Parkinson realized he would need a diagram to explain his ideas so made a quick sketch on a sheet of plain white typingpaper.
The company submitted a proposal for exploratory work on an electromechanical system for directing antiaircraft guns to the Army Signal Corps which was subsequently approved. An engineering model was delivered for testing to the Army at Fort Monroe MD on 1 December 1941. The result of Parkinson's dream began rolling off the assembly lines early in 1943. More than 3000 of the gun directors, designated the M-9, were built.
Many thousands of shells were fired to bring down a single aircraft with the older directors; the M9 brought the number down to around 100 shells per hit on an aircraft.
Thus Parkinson's unconscious revelation led to one of the most effective pieces of air-defense technology in World War II.

Green Bay Press Gazette - Apr 22, 1947
Posted By: Alex - Thu Oct 08, 2020 -
Comments (3)
Category: Sleep and Dreams, 1940s, Weapons
Caccolube
Or, how to ruin an engine, courtesy of the OSS."When circulated through this system, the compound fuses and welds the moving metal parts of the machinery. Slipped into a truck, the Caccolube takes effect after the truck has been driven from 30 to 50 miles. It reacts so thoroughly on pistons, cylinder walls and bearing journals that the vehicle is not only thrown out of service but the engine is destroyed beyond repair."
This lethal "lube job" replaced the original effort using sugar, when it was discovered that sugar actually promoted better engine performance in the vehicles of that era.
Source: Jack Anderson, "Rare arsenal used by spies," Santa Cruz Sentinel, Mar 9, 1987.
Posted By: Alex - Sat Sep 12, 2020 -
Comments (1)
Category: Motor Vehicles, War, Weapons, Spies and Intelligence Services
Remove the braces, or else…
I'm sure this must have been the strangest day in Norman Carstens' career as an orthodontist:"I had him in the chair and he leaned over and pulled the gun out of his pocket and said, 'Would this make you change your mind?' and I said, 'Yes,'" Carstens said.

(click to enlarge)
Central New Jersey Home News - Feb 16, 1985
Posted By: Alex - Thu Sep 10, 2020 -
Comments (0)
Category: 1980s, Weapons, Teeth
The Holie Terra
Seeking a way to use technology to win the tunnel warfare in Vietnam, Nelson Frost of Byram, Connecticut invented the "Holie Terra." Although in the write-up for the patent he received (No. 3,395,641), he referred to it more formally as a "remotely controlled tunnel exploration and destroying means."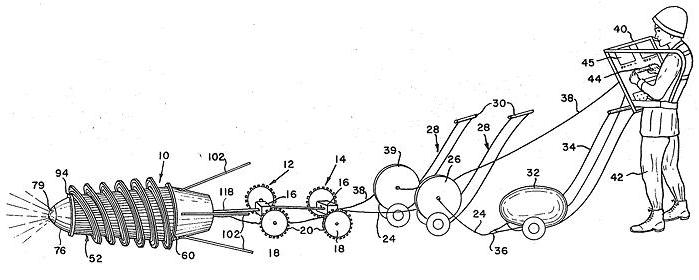
From his patent:
More particularly, it is an object of the invention to provide a tunnel exploring device which may be maneuvered from a remote position deep into the tunnel network and there be detonated so that there is a much higher kill probability of the enemy forces with greater safety to the attackers than has been possible by any means employed heretofore.


Montgomery Advertiser - Aug 15, 1968
Posted By: Alex - Sun Aug 23, 2020 -
Comments (2)
Category: War, Weapons, Patents, 1960s
The man whom bullets bounced off of
In 1976, King Dixon of Miami was shot five times at close range in the head during a bar fight. Not a single bullet penetrated his skull. He was hospitalized overnight for observation, and then released the following day in satisfactory condition.
Alexandria Town Talk - May 10, 1976

Casper Star-Tribune - May 12, 1976
It seemed at the time like he must have been bulletproof, but a follow-up by Miami Herald crime reporter Edna Buchanan, in her book Never Let Them See You Cry, reveals that he was affected by bullets after all:
But the bullets did kill him. I found King Dixon at the morgue eight years later. Since the shooting he had suffered seizures, and one of them killed him.
The medical examiner blamed the old bullet wounds and ruled the death a homicide.
King Dixon became Miami's only murder victim in 1984 killed by bullets fired in 1976.
Posted By: Alex - Fri Jun 12, 2020 -
Comments (2)
Category: Crime, Human Marvels, 1970s, Weapons

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




