Psychology
Noses
Read it here.

Posted By: Paul - Fri Jan 20, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Body, Science, Psychology, Self-help Schemes, 1950s
Asneezia
In a 1985 report published in the British Journal of Psychiatry, Dr. G.D. Shukla brought a new condition to the attention of the medical community — the inability to sneeze. He named this 'Asneezia'. The sufferers were 'Asneezics'. His original article is behind a paywall, but a summary from Brain/Mind Bulletin is below:
Brain/Mind Bulletin - July 1990
Later correspondents to the British Journal of Psychiatry were skeptical. One questioned whether Shukla's patients really suffered from this condition, or if they were simply delusional. Another proposed verifying the reality of Asneezia by exposing patients to "the most noxious inhalant allergen."
Posted By: Alex - Fri Oct 21, 2022 -
Comments (2)
Category: Health, Psychology
Hi-Fi Addiction
Back in 1957, Dr. H. Angus Bowes argued that many Hi-Fi enthusiasts were, in fact, addicted to their music systems in an unhealthy way. I'm sure there are still people today who exhibit similar symptoms.One addict said he would not be satisfied until he could hear the drip of saliva from the French horns as they were emptied after a powerful brass passage, Dr. Bowes reported.

El Paso Herald-Post - Apr 15, 1957
Posted By: Alex - Wed Oct 19, 2022 -
Comments (2)
Category: Music, Psychology, 1950s
Another Miss Psy War
I looked through an online newspaper archive to see if I could find out anything about those "Miss Psywar" photos Paul posted two days ago. I didn't. But I did come across another Miss Psywar.Bonnie Halpin was chosen as "Miss Psy War of 1962" by the 349th Psychological Warfare Company.

Arlington Heights Herald - July 12, 1962
Halpin, it turns out, is a minor celebrity. She had the distinction of being the very first Playboy bunny ever. She also appeared on the cover of the Oct 1962 issue of Playboy magazine. Unfortunately she died in 2004 at the relatively young age of 65.
More info about Halpin: FindAGrave.com


Hackensack Record - Apr 30, 2004
Posted By: Alex - Thu Aug 25, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Awards, Prizes, Competitions and Contests, Psychology, 1960s, Armed Forces
Does college turn young women into communists?
Back in the 1930s families were concerned about whether they should send their young daughters off to college, fearing they might come home infected with communism. So in 1934, psychologist Stephen M. Corey set out to determine whether such fears were justified.Corey administered the Thurstone Attitude Scale to 234 female freshmen at the University of Wisconsin, examining their attitudes with respect to six topics: Reality of God, War, Patriotism, Communism, Evolution, and Church. A year later he retested 100 of these students when they were sophomores.

Godless communists?
When he presented his findings at the Midwestern Psychological Association convention in May 1940, he assured everyone that it was safe to send young women to college, saying, "There was no great difference in the girls' attitudes. The average co-ed apparently would rather mix with stag lines than picket lines."
He also emphasized that the young women lost none of their feminine habits at college. A United Press reporter paraphrased his words:
However, if you look at his 1940 article in the Journal of Social Psychology*, in which he published the results of his study, you find somewhat different information. There he revealed that after a year at college the attitudes of the young women did change slightly, but consistently, in the direction of liberalism — which is to say that they showed less sympathy for god, war, patriotism, and the church, and more sympathy for communism and evolution.
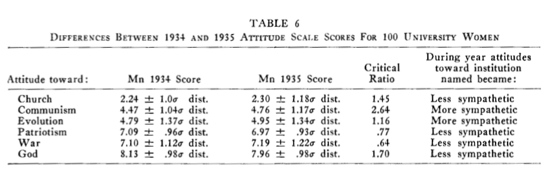
Corey wrote in that article, "The opinions of the students appeared to have undergone at least a degree of liberalization during their one year of attendance at a University."
I guess he wasn't actually lying to the folks at the Midwestern Psychological Association. It's all how you choose to spin the data.

San Bernardino County Sun - May 5, 1940
* Corey, S.M. (1940). "Changes in the opinions of female students after one year at university." The Journal of Social Psychology, 11: 341-351.
Posted By: Alex - Wed Aug 17, 2022 -
Comments (4)
Category: Psychology, 1930s, Women, Universities, Colleges, Private Schools and Academia
The Sauna Bath Nymphomaniac
The case of the cable car nymphomaniac is a classic weird news story. Less well known, but along similar lines, is the case of the sauna bath nymphomaniac.Maria Parson claimed that the trauma of being accidentally locked in a sauna for half-an-hour due to a faulty door handle caused her to develop a split personality. She came to have three personalities: "sex-hungry Maria" who prowled bars picking up men, "remorseful Betty" who bitterly resented Maria's escapades, and her submerged real self.
She sued the health spa for $1 million, but lost — even though she was represented by the same lawyer who had secured a win for the cable car nymphomaniac.

Orange Coast Pilot - Dec 20, 1973
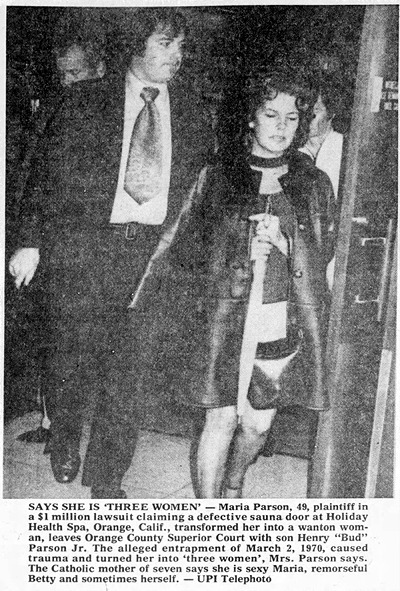

Bellingham Herald - Jan 10, 1974

Eureka Times Standard - Mar 6, 1974
Posted By: Alex - Wed Apr 20, 2022 -
Comments (1)
Category: Lawsuits, Psychology, 1970s, Sex
Care Bear Abuse
Feb 1987: Wanting to do something special for her son, Jeania Denny wore a Care Bear costume to his school on Valentine's Day. However, she soon found herself being violently attacked by a crowd of sixth-graders. Said Denny, "I kept yelling at them to stop, that they were hurting me, but the more I yelled the more they attacked."I've heard reports of children (and adults) at Disney theme parks hitting the costumed characters, which seems similar to what happened to Jeania Denny. In the minds of the children, the costume must dehumanize the wearer, which then makes it seem okay to hit them.

Tampa Bay Times - Feb 17, 1987
I'm guessing this was the type of costume that Denny was wearing:

Posted By: Alex - Sun Jan 30, 2022 -
Comments (6)
Category: Violence, Psychology, 1980s
The Case of the Furious Children
In 1954, six young boys who exhibited violent behavior were brought to live on the grounds of the National Institute of Health in Bethesda, Maryland. They were specifically selected because they were deemed the worst of the worst:For the next five years, the boys were attended around the clock by a team of specialists.
It was all part of an experiment, which came to be known as the "Case of the Furious Children," designed to find out why these young boys were so violent and whether they could be turned into responsible citizens. Eventually, around $1.5 million (in 1950's dollars) was spent on this effort.
By the end of the experiment, one of the researchers, Dr. Nicholas Long, said that the boys now had a "better than 50-50 chance of living a productive life." So what became of them? Were they reformed, or did they head down the path of crime and prison that they originally seemed to be destined for?
I'd be interesting to know, but I haven't been able to find anything out. I'm guessing the info has never been released because of privacy issues.
More info: Harpers Magazine - Jan 1958

Chicago Daily Tribune - July 19, 1959
Posted By: Alex - Wed Jan 19, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Antisocial Activities, Experiments, Psychology, Children, 1950s
The Fainting of the Tigerettes
Sep 12, 1952: At the end of the first quarter of a high-school football game in Natchez, Mississippi, the 165 members of the Tigerettes cheerleading squad mistakenly marched onto the field to perform their halftime routine. Made aware of their mistake, the cheerleaders began to faint. All of them. One after another. A witness described them as "dropping out like flies". It remains one of the largest mass-fainting events in history.

Shreveport Journal - Sep 13, 1952
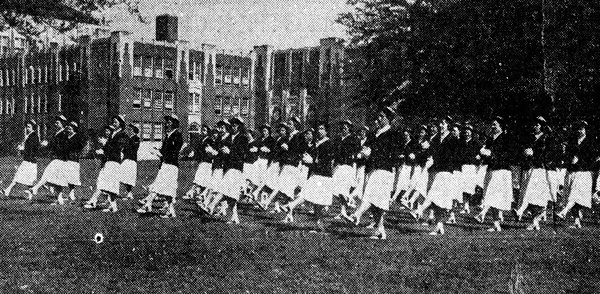
The Tigerettes
Monroe Morning World - Apr 27, 1952
Posted By: Alex - Thu Dec 09, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Crowds, Groups, Mobs and Other Mass Movements, Psychology, 1950s
The Voice Bomb
This is another example of the military's interest in using sound to demoralize the enemy. This device was rather straightforward: "Dropped from a plane, the balloon bomb would drift to earth while the recorder blared out surrender demands or other morale-breaking messages to the enemy."See also: Weird alien sounds designed to terrify and panic, and Ghost Tape Number Ten
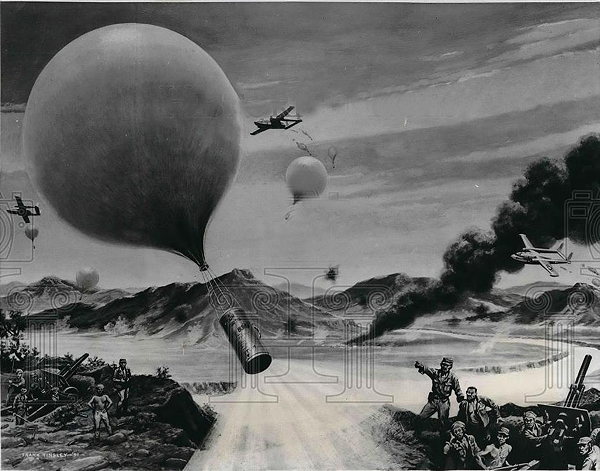

The Pantagraph - Oct 12, 1951
Posted By: Alex - Tue Sep 07, 2021 -
Comments (4)
Category: Psychology, 1950s, Weapons

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




